Type 2 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor in the ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus is critical in regulating feeding and lipid metabolism in white adipose tissue
- PMID: 22067315
- PMCID: PMC3249673
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2011-1312
Type 2 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor in the ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus is critical in regulating feeding and lipid metabolism in white adipose tissue
Abstract
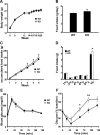
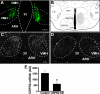
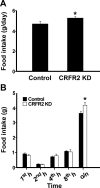
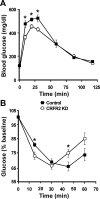
Ventromedial nucleus of hypothalamus (VMH) plays a critical role in regulating feeding and energy metabolism. The nucleus expresses high levels of the type 2 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor (CRFR2) and receives prominent innervation of nerve fibers containing Urocortin 3 (Ucn 3), an endogenous ligand of the receptor. In the present study, we showed that mice deficient in Ucn 3 had elevated basal feeding and increased nocturnal food intake after overnight fasting compared with the wild-type (WT) littermates. The Ucn 3 null mice also had lower circulating insulin levels compared with those of the WT mice. Interestingly, the mutant mice maintained a comparable body weight with the WT littermates. Mice with reduced CRFR2 expression in the VMH by small hairpin RNA knockdown (KD) recapitulated feeding phenotypes observed in the Ucn 3 null mice. However, VMH CRFR2 KD mice gained significantly more weight than control mice. The weight gain was due to an accumulation of white adipose tissue (WAT) accompanied by reduced plasma free fatty acids and glycerol levels, increased respiratory quotients, and improved glucose tolerance. On the other hand, plasma insulin levels were comparable with the receptor KD and control mice. Furthermore, the expression of several genes, including hormone-sensitive lipase, was significantly reduced in the WAT of VMH CRFR2 KD mice compared with controls. These results indicate that Ucn 3 signaling through CRFR2 is a critical molecular mediator in the VMH in regulating feeding and lipid metabolism in WAT.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Injection of Urocortin 3 into the ventromedial hypothalamus modulates feeding, blood glucose levels, and hypothalamic POMC gene expression but not the HPA axis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Feb;298(2):E337-45. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00402.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 19952342 Free PMC article.
-
Urocortins and corticotropin releasing factor type 2 receptors in the hypothalamus and the cardiovascular system.Peptides. 2004 Oct;25(10):1711-21. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.05.024. Peptides. 2004. PMID: 15476938 Review.
-
Hypothalamic expression of urocortin 3 and the type 2 corticotropin-releasing factor receptor is regulated according to feeding state in lean but not obese Zucker rats.Neuropharmacology. 2012 Jul;63(1):147-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.12.023. Epub 2011 Dec 26. Neuropharmacology. 2012. PMID: 22227020
-
Urocortin 3 transgenic mice exhibit a metabolically favourable phenotype resisting obesity and hyperglycaemia on a high-fat diet.Diabetologia. 2011 Sep;54(9):2392-403. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2205-6. Epub 2011 Jun 11. Diabetologia. 2011. PMID: 21667214 Free PMC article.
-
The rise, fall, and resurrection of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the regulation of feeding behavior and body weight.Physiol Behav. 2006 Feb 28;87(2):221-44. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.10.007. Epub 2006 Jan 18. Physiol Behav. 2006. PMID: 16412483 Review.
Cited by
-
Centrally Projecting Edinger-Westphal Nucleus in the Control of Sympathetic Outflow and Energy Homeostasis.Brain Sci. 2021 Jul 29;11(8):1005. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11081005. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34439626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urocortin Neuropeptide Levels Are Impaired in the PBMCs of Overweight Children.Nutrients. 2022 Jan 18;14(3):429. doi: 10.3390/nu14030429. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35276788 Free PMC article.
-
Brain regulation of energy balance and body weight.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013 Dec;14(4):387-407. doi: 10.1007/s11154-013-9261-9. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013. PMID: 23990408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of stresscopin on rat hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus neurons in vitro.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53863. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053863. Epub 2013 Jan 18. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23349753 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular mechanisms of synchronized rhythmic burst generation in the ventromedial hypothalamus.Pflugers Arch. 2025 Jan;477(1):131-145. doi: 10.1007/s00424-024-03031-x. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Pflugers Arch. 2025. PMID: 39400580
References
-
- Lewis K, Li C, Perrin MH, Blount A, Kunitake K, Donaldson C, Vaughan J, Reyes TM, Gulyas J, Fischer W, Bilezikjian L, Rivier J, Sawchenko PE, Vale WW. 2001. Identification of urocortin III, an additional member of the corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) family with high affinity for the CRF2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7570–7575 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsu SY, Hsueh AJ. 2001. Human stresscopin and stresscopin-related peptide are selective ligands for the type 2 corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor. Nat Med 7:605–611 - PubMed
-
- Li C, Chen P, Vaughan J, Blount A, Chen A, Jamieson PM, Rivier J, Smith MS, Vale W. 2003. Urocortin III is expressed in pancreatic β-cells and stimulates insulin and glucagon secretion. Endocrinology 144:3216–3224 - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Totsune K, Saruta M, Fukuda T, Suzuki T, Hirose T, Imai Y, Sasano H, Murakami O. 2006. Expression of urocortin 3/stresscopin in human adrenal glands and adrenal tumors. Peptides 27:178–182 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

