Cognitive decline typical of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in transgenic mice expressing the 25-kDa C-terminal fragment of TDP-43
- PMID: 22067910
- PMCID: PMC3338346
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.09.022
Cognitive decline typical of frontotemporal lobar degeneration in transgenic mice expressing the 25-kDa C-terminal fragment of TDP-43
Abstract
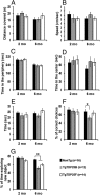
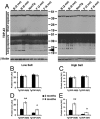
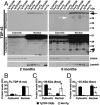
Transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) is the pathological signature protein in several neurodegenerative disorders, including the majority of frontotemporal lobar degeneration cases (FTLD-TDP), motor neuron disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Pathological TDP-43 is mislocalized from its nuclear location to the cytoplasm, where it accumulates and is proteolytically cleaved to form C-terminal fragments. Although the 25-kDa C-terminal fragment of TDP-43 (TDP-25) accumulates in affected brain regions, its role in the disease pathogenesis remains elusive. To address this problem, we have generated a novel transgenic mouse that selectively expresses TDP-25 in neurons. We show that transgenic mice expressing TDP-25 develop cognitive deficits associated with the build-up of soluble TDP-25. These cognitive deficits are independent of TDP-43-positive inclusions and occur without overt neurodegeneration. Additionally, we show that the expression of TDP-25 is sufficient to alter the processing of endogenous full-length TDP-43. These studies represent the first in vivo demonstration of a pathological role for TDP-25 and strongly suggest that the onset of cognitive deficits in TDP-43 proteinopathies is independent of TDP-43 inclusions. These data provide a framework for understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the onset of cognitive deficits in FTLD-TDP and other TDP-43 proteinopathies; thus, the TDP-25 transgenic mice represent a unique tool to reach this goal.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
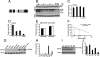

References
-
- Wang H.Y., Wang I.F., Bose J., Shen C.K. Structural diversity and functional implications of the eukaryotic TDP gene family. Genomics. 2004;83:130–139. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E., Baralle F.E. Characterization and functional implications of the RNA binding properties of nuclear factor TDP-43, a novel splicing regulator of CFTR exon 9. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36337–36343. - PubMed
-
- Buratti E., Baralle F.E. Multiple roles of TDP-43 in gene expression, splicing regulation, and human disease. Front Biosci. 2008;13:867–878. - PubMed
-
- Wang I.F., Wu L.S., Chang H.Y., Shen C.K. TDP-43, the signature protein of FTLD-U, is a neuronal activity-responsive factor. J Neurochem. 2008;105:797–806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

