An indirect role for ASPP1 in limiting p53-dependent p21 expression and cellular senescence
- PMID: 22068052
- PMCID: PMC3261561
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.402
An indirect role for ASPP1 in limiting p53-dependent p21 expression and cellular senescence
Abstract
In addition to acting as a transcriptional cofactor for p53, ASPP1 has been shown to function in the cytoplasm to regulate the nuclear localization and activity of YAP/TAZ. We show here that the ability of ASPP1 to activate YAP results in the decreased expression of LATS2, which lowers the ability of p53 to induce p21, cell-cycle arrest and senescence. ASPP1 expression peaks in S-phase, and down-regulation of ASPP1 leads to a reduction in DNA synthesis and enhanced senescence in response to drugs that impede DNA replication. These activities of cytoplasmic ASPP1 in opposing p53-mediated p21 expression are in contrast to the role of nuclear ASPP1 in cooperating with p53 to induce the expression of apoptotic target genes, and may help to dampen p53 activity in normal cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
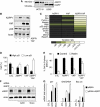

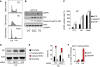
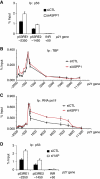


Similar articles
-
Cytoplasmic ASPP1 inhibits apoptosis through the control of YAP.Genes Dev. 2010 Nov 1;24(21):2430-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1954310. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 21041411 Free PMC article.
-
The Lats2 tumor suppressor augments p53-mediated apoptosis by promoting the nuclear proapoptotic function of ASPP1.Genes Dev. 2010 Nov 1;24(21):2420-9. doi: 10.1101/gad.1954410. Genes Dev. 2010. PMID: 21041410 Free PMC article.
-
ASPP1 and ASPP2: common activators of p53 family members.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;24(3):1341-50. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.3.1341-1350.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 14729977 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and autophagy: Regulation of apoptosis by DNA damage signalling - roles of p53, p73 and HIPK2.FEBS J. 2009 Nov;276(21):6074-83. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07331.x. Epub 2009 Sep 29. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19788416 Review.
-
[Molecular mechanisms controlling the cell cycle: fundamental aspects and implications for oncology].Cancer Radiother. 2001 Apr;5(2):109-29. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(01)00087-7. Cancer Radiother. 2001. PMID: 11355576 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The LATS1 and LATS2 tumor suppressors: beyond the Hippo pathway.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Sep;24(9):1488-1501. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.99. Epub 2017 Jun 23. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28644436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asparaginase treatment side-effects may be due to genes with homopolymeric Asn codons (Review-Hypothesis).Int J Mol Med. 2015 Sep;36(3):607-26. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2285. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 26178806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 shades of Hippo.Cell Death Differ. 2018 Jan;25(1):81-92. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.163. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Cell Death Differ. 2018. PMID: 28984872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The feedback loop of ANKHD1/lncRNA MALAT1/YAP1 strengthens the radioresistance of CRC by activating YAP1/AKT signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Feb 2;13(2):103. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04554-w. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35110552 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting Expression of Hippo Effector, Yap, for Expansion of Functional Islet Mass.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Nov;29(11):1594-607. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1375. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26378466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansieau S, Morel AP, Hinkal G, Bastid J, Puisieux A (2010) TWISTing an embryonic transcription factor into an oncoprotein. Oncogene 29: 3173–3184 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

