Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering with N-Acyl functionalized ManNAc analogs: cytotoxicity, metabolic flux, and glycan-display considerations
- PMID: 22068462
- PMCID: PMC3288793
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.24363
Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering with N-Acyl functionalized ManNAc analogs: cytotoxicity, metabolic flux, and glycan-display considerations
Abstract
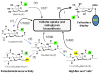
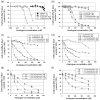
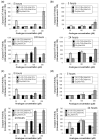
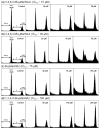
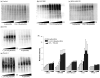
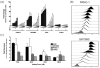
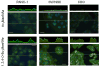
Metabolic oligosaccharide engineering (MOE) is a maturing technology capable of modifying cell surface sugars in living cells and animals through the biosynthetic installation of non-natural monosaccharides into the glycocalyx. A particularly robust area of investigation involves the incorporation of azide functional groups onto the cell surface, which can then be further derivatized using "click chemistry." While considerable effort has gone into optimizing the reagents used for the azide ligation reactions, less optimization of the monosaccharide analogs used in the preceding metabolic incorporation steps has been done. This study fills this void by reporting novel butanoylated ManNAc analogs that are used by cells with greater efficiency and less cytotoxicity than the current "gold standard," which are peracetylated compounds such as Ac₄ ManNAz. In particular, tributanoylated, N-acetyl, N-azido, and N-levulinoyl ManNAc analogs with the high flux 1,3,4-O-hydroxyl pattern of butanoylation were compared with their counterparts having the pro-apoptotic 3,4,6-O-butanoylation pattern. The results reveal that the ketone-bearing N-levulinoyl analog 3,4,6-O-Bu₃ ManNLev is highly apoptotic, and thus is a promising anti-cancer drug candidate. By contrast, the azide-bearing analog 1,3,4-O-Bu₃ ManNAz effectively labeled cellular sialoglycans at concentrations ∼3- to 5-fold lower (e.g., at 12.5-25 µM) than Ac₄ ManNAz (50-150 µM) and exhibited no indications of apoptosis even at concentrations up to 400 µM. In summary, this work extends emerging structure activity relationships that predict the effects of short chain fatty acid modified monosaccharides on mammalian cells and also provides a tangible advance in efforts to make MOE a practical technology for the medical and biotechnology communities.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the metabolic flux and apoptotic effects of O-hydroxyl- and N-acyl-modified N-acetylmannosamine analogs in Jurkat cells.J Biol Chem. 2004 Apr 30;279(18):18342-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M400205200. Epub 2004 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14966124
-
Switching azide and alkyne tags on bioorthogonal reporters in metabolic labeling of sialylatedglycoconjugates: a comparative study.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 22;12(1):22129. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26521-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36550357 Free PMC article.
-
Regioisomeric SCFA attachment to hexosamines separates metabolic flux from cytotoxicity and MUC1 suppression.ACS Chem Biol. 2008 Apr 18;3(4):230-40. doi: 10.1021/cb7002708. Epub 2008 Mar 14. ACS Chem Biol. 2008. PMID: 18338853
-
Biochemical engineering of the N-acyl side chain of sialic acid: biological implications.Glycobiology. 2001 Feb;11(2):11R-18R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/11.2.11r. Glycobiology. 2001. PMID: 11287396 Review.
-
Hexosamine analogs: from metabolic glycoengineering to drug discovery.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009 Dec;13(5-6):565-72. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2009.08.001. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2009. PMID: 19747874 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating antibody N-glycosylation through feed additives using a multi-tiered approach.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Aug 26;12:1448925. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1448925. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39253702 Free PMC article.
-
Facile metabolic glycan labeling strategy for exosome tracking.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018 May;1862(5):1091-1100. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2018. PMID: 29410228 Free PMC article.
-
Production of site-specific antibody conjugates using metabolic glycoengineering and novel Fc glycovariants.J Biol Chem. 2024 Dec;300(12):108005. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.108005. Epub 2024 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39551135 Free PMC article.
-
Butyrate histone deacetylase inhibitors.Biores Open Access. 2012 Aug;1(4):192-8. doi: 10.1089/biores.2012.0223. Biores Open Access. 2012. PMID: 23514803 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical reporters to study mammalian O-glycosylation.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Apr 30;49(2):903-913. doi: 10.1042/BST20200839. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 33860782 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aich U, Campbell CT, Elmouelhi N, Weier CA, Sampathkumar SG, Choi SS, Yarema KJ. Regioisomeric SCFA attachment to hexosamines separates metabolic flux from cytotoxicity and MUC1 suppression. ACS Chem Biol. 2008;3:230–240. - PubMed
-
- Aich U, Meledeo MA, Sampathkumar SG, Fu J, Jones MB, Weier CA, Chung SY, Tang BC, Yang M, Hanes J, Yarema KJ. Development of delivery methods for carbohydrate-based drugs: controlled release of biologically-active short chain fatty acid-hexosamine analogs. Glycoconjug J. 2010;27:445–459. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arden N, Nivitchanyong T, Betenbaugh MJ. Cell engineering blocks cell stress and improves biotherapeutic production. Bioprocess J. 2004 March/April;:23–28.
-
- Benjamin CW, Hiebsch RR, Jones DA. Caspase activation in MCF7 cells responding to etoposide treatment. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;53:446–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

