124I-huA33 antibody uptake is driven by A33 antigen concentration in tissues from colorectal cancer patients imaged by immuno-PET
- PMID: 22068895
- PMCID: PMC3394180
- DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.111.095596
124I-huA33 antibody uptake is driven by A33 antigen concentration in tissues from colorectal cancer patients imaged by immuno-PET
Abstract
The primary aim of this analysis was to examine the quantitative features of antibody-antigen interactions in tumors and normal tissue after parenteral administration of antitumor antibodies to human patients.
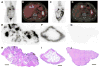
Methods: Humanized anti-A33 antibody (10 mg) labeled with the positron-emitting radionuclide (124)I ((124)I-huA33) was injected intravenously in 15 patients with colorectal cancer. Clinical PET/CT was performed approximately 1 wk later, followed by a detailed assay of surgically removed tissue specimens including radioactivity counting, autoradiography, immunohistochemistry, and antigen density determination.
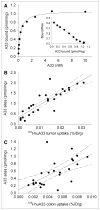
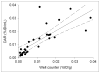
Results: PET/CT showed high levels of antibody targeting in tumors and normal bowel. In tissue specimens, the spatial distribution of (124)I-huA33 conformed to that of A33 antigen, and there was a linear relationship between the amount of bound antibody and antigen concentration. Antibody uptake was high in 1- to 2-mm regions of antigen-positive tumor cells (mean, ~0.05 percentage injected dose per gram) and in antigen-positive normal colonic mucosa (mean, ~0.03 percentage injected dose per gram). The estimated binding site occupancy for tumor and normal colon was 20%-50%.
Conclusion: The in vivo biodistribution of (124)I-huA33 in human patients 1 wk after antibody administration was determined by A33 antigen expression. Our data imply that the optimal strategy for A33-based radioimmunotherapy of colon cancer will consist of a multistep treatment using a radionuclide with short-range (α- or β-particle) emissions.
Conflict of interest statement
No other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Garinchesa P, Sakamoto J, Welt S, Real FX, Rettig WJ, Old LJ. Organ-specific expression of the colon cancer antigen A33, a cell surface target for antibody-based therapy. Int J Oncol. 1996;9:465–471. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone CN, White SJ, Tebbutt NC, et al. Analysis of the regulation of the A33 antigen gene reveals intestine-specific mechanisms of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:34531–34539. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto J, Kojima H, Kato J, Hamashima H, Suzuki H. Organ-specific expression of the intestinal epithelium-related antigen A33, a cell surface target for antibody-based imaging and treatment in gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2000;46:S27–S32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
