Direct interaction between scaffolding proteins RACK1 and 14-3-3ζ regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) transcription
- PMID: 22069327
- PMCID: PMC3249084
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.272195
Direct interaction between scaffolding proteins RACK1 and 14-3-3ζ regulates brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) transcription
Abstract
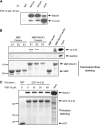
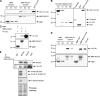
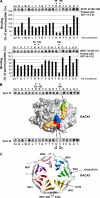
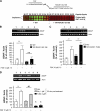
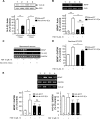
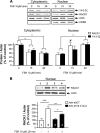
RACK1 is a scaffolding protein that spatially and temporally regulates numerous signaling cascades. We previously found that activation of the cAMP signaling pathway induces the translocation of RACK1 to the nucleus. We further showed that nuclear RACK1 is required to promote the transcription of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Here, we set out to elucidate the mechanism underlying cAMP-dependent RACK1 nuclear translocation and BDNF transcription. We identified the scaffolding protein 14-3-3ζ as a direct binding partner of RACK1. Moreover, we found that 14-3-3ζ was necessary for the cAMP-dependent translocation of RACK1 to the nucleus. We further observed that the disruption of RACK1/14-3-3ζ interaction with a peptide derived from the RACK1/14-3-3ζ binding site or shRNA-mediated 14-3-3ζ knockdown inhibited cAMP induction of BDNF transcription. Together, these data reveal that the function of nuclear RACK1 is mediated through its interaction with 14-3-3ζ. As RACK1 and 14-3-3ζ are two multifunctional scaffolding proteins that coordinate a wide variety of signaling events, their interaction is likely to regulate other essential cellular functions.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

