An inducible cell-cell fusion system with integrated ability to measure the efficiency and specificity of HIV-1 entry inhibitors
- PMID: 22069466
- PMCID: PMC3206054
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026731
An inducible cell-cell fusion system with integrated ability to measure the efficiency and specificity of HIV-1 entry inhibitors
Abstract
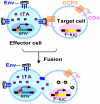
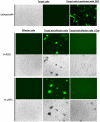
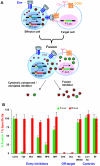
HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins (Envs) mediate virus entry by fusing the viral and target cell membranes, a multi-step process that represents an attractive target for inhibition. Entry inhibitors with broad-range activity against diverse isolates of HIV-1 may be extremely useful as lead compounds for the development of therapies or prophylactic microbicides. To facilitate the identification of such inhibitors, we have constructed a cell-cell fusion system capable of simultaneously monitoring inhibition efficiency and specificity. In this system, effector cells stably express a tetracycline-controlled transactivator (tTA) that enables tightly inducible expression of both HIV-1 Env and the Renilla luciferase (R-Luc) reporter protein. Target cells express the HIV-1 receptors, CD4 and CCR5, and carry the firefly luciferase (F-Luc) reporter gene under the control of a tTA-responsive promoter. Thus, Env-mediated fusion of these two cell types allows the tTA to diffuse to the target cell and activate the expression of the F-Luc protein. The efficiency with which an inhibitor blocks cell-cell fusion is measured by a decrease in the F-Luc activity, while the specificity of the inhibitor is evaluated by its effect on the R-Luc activity. The system exhibited a high dynamic range and high Z'-factor values. The assay was validated with a reference panel of inhibitors that target different steps in HIV-1 entry, yielding inhibitory concentrations comparable to published virus inhibition data. Our system is suitable for large-scale screening of chemical libraries and can also be used for detailed characterization of inhibitory and cytotoxic properties of known entry inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


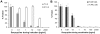

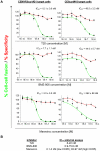
References
-
- Barre-Sinoussi F, Chermann JC, Rey F, Nugeyre MT, Chamaret S, et al. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983;220:868–871. - PubMed
-
- Gallo RC, Salahuddin SZ, Popovic M, Shearer GM, Kaplan M, et al. Frequent detection and isolation of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science. 1984;224:500–503. - PubMed
-
- Mehellou Y, De Clercq E. Twenty-six years of anti-HIV drug discovery: where do we stand and where do we go? J Med Chem. 2010;53:521–538. - PubMed
-
- Arenas-Pinto A, Grant A, Bhaskaran K, Copas A, Carr A, et al. Risk factors for fatality in HIV-infected patients with dideoxynucleoside-induced severe hyperlactataemia or lactic acidosis. Antivir Ther. 2011;16:219–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

