Potentiometric sensors based on fluorous membranes doped with highly selective ionophores for carbonate
- PMID: 22070518
- PMCID: PMC3244523
- DOI: 10.1021/ja207680e
Potentiometric sensors based on fluorous membranes doped with highly selective ionophores for carbonate
Abstract
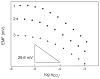
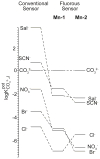
Manganese(III) complexes of three fluorophilic salen derivatives were used to prepare ion-selective electrodes (ISEs) with ionophore-doped fluorous sensing membranes. Because of their extremely low polarity and polarizability, fluorous media are not only chemically very inert but also solvate potentially interfering ions poorly, resulting in a much improved discrimination of such ions. Indeed, the new ISEs exhibited selectivities for CO(3)(2-) that exceed those of previously reported ISEs based on nonfluorous membranes by several orders of magnitude. In particular, the interference from chloride and salicylate was reduced by 2 and 6 orders of magnitude, respectively. To achieve this, the selectivities of these ISEs were fine-tuned by addition of noncoordinating hydrophobic ions (i.e., ionic sites) into the sensing membranes. Stability constants of the anion-ionophore complexes were determined from the dependence of the potentiometric selectivities on the charge sign of the ionic sites and the molar ratio of ionic sites and the ionophore. For this purpose, a previously introduced fluorophilic tetraphenylborate and a novel fluorophilic cation with a bis(triphenylphosphoranylidene)ammonium group, (R(f6)(CH(2))(3))(3)PN(+)P(R(f6)(CH(2))(3))(3), were utilized (where R(f6) is C(6)F(13)). The optimum CO(3)(2-) selectivities were found for sensing membranes composed of anionic sites and ionophore in a 1:4 molar ratio, which results in the formation of 2:1 complexes with CO(3)(2-) with stability constants up to 4.1 × 10(15). As predicted by established theory, the site-to-ionophore ratios that provide optimum potentiometric selectivity depend on the stoichiometries of the complexes of both the primary and the interfering ions. However, the ionophores used in this study give examples of charges and stoichiometries previously neither explicitly predicted by theory nor shown by experiment. The exceptional selectivity of fluorous membranes doped with these carbonate ionophores suggests their use not only for potentiometric sensing but also for other types of sensors, such as the selective separation of carbonate from other anions and the sequestration of carbon dioxide.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures



Similar articles
-
Highly selective detection of silver in the low ppt range with ion-selective electrodes based on ionophore-doped fluorous membranes.Anal Chem. 2010 Sep 15;82(18):7634-40. doi: 10.1021/ac1013767. Anal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20799720 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorophilic ionophores for potentiometric pH determinations with fluorous membranes of exceptional selectivity.Anal Chem. 2008 Mar 15;80(6):2084-90. doi: 10.1021/ac702161c. Epub 2008 Feb 22. Anal Chem. 2008. PMID: 18290670
-
Fluorous polymeric membranes for ionophore-based ion-selective potentiometry: how inert is Teflon AF?J Am Chem Soc. 2009 Feb 4;131(4):1598-1606. doi: 10.1021/ja808047x. J Am Chem Soc. 2009. PMID: 19133768 Free PMC article.
-
History of Cobaltabis(dicarbollide) in Potentiometry, No Need for Ionophores to Get an Excellent Selectivity.Molecules. 2022 Nov 29;27(23):8312. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238312. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500404 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern potentiometry.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46(30):5660-8. doi: 10.1002/anie.200605068. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007. PMID: 17457791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ion-selective electrodes with unusual response functions: simultaneous formation of ionophore-primary ion complexes with different stoichiometries.Anal Chem. 2012 Jan 17;84(2):1104-11. doi: 10.1021/ac202761x. Epub 2011 Dec 22. Anal Chem. 2012. PMID: 22128799 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamental investigation on fluorous nanoemulsion optodes: effect of matrix fluorination on selectivity.Anal Sci. 2024 Sep;40(9):1787-1792. doi: 10.1007/s44211-024-00603-w. Epub 2024 May 25. Anal Sci. 2024. PMID: 38795277
-
Flexible Acetylcholine Neural Probe with a Hydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene Electrode and a Fluorous-Phase Sensing Membrane.ACS Mater Lett. 2024 Sep 2;6(9):4158-4167. doi: 10.1021/acsmaterialslett.4c00825. Epub 2024 Aug 15. ACS Mater Lett. 2024. PMID: 39309214 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorous-Phase Ion-Selective pH Electrodes: Electrode Body and Ionophore Optimization for Measurements in the Physiological pH Range.ACS Omega. 2020 Jun 1;5(23):13621-13629. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00582. eCollection 2020 Jun 16. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 32566827 Free PMC article.
-
Turn Off-On Fluorescent CO2 Gas Detection Based on Amine-Functionalized Imidazole-Based Poly(ionic liquid).ACS Omega. 2022 Oct 27;7(44):40485-40492. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05695. eCollection 2022 Nov 8. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36385837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molly D, Nogue-Vila X. CAP today. 2009;23:24–40.
-
- Severinghaus JW, Bradley AF. J Appl Physiol. 1958;13:515. - PubMed
-
- Morf WE. The Principles of Ion-selective Electrodes and of Membrane Transport. Elsevier; New York, NY: 1981.
-
- Bakker E, Bühlmann P, Pretsch E. Chem Rev. 1997;97:3083–3132. - PubMed
-
- Bühlmann P, Chen LD. Ion-Selective Electrodes with Ionophore-Doped Sensing Membranes. In: Gale PA, Steed JW, editors. Supramolecular Chemistry: From Molecules to Nanomaterials; Wiley; New York, NY: 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

