Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients
- PMID: 22071799
- PMCID: PMC7055200
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001208.pub4
Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients
Abstract
Background: Human albumin solutions are used for a range of medical and surgical problems. Licensed indications are the emergency treatment of shock and other conditions where restoration of blood volume is urgent, such as in burns and hypoproteinaemia. Human albumin solutions are more expensive than other colloids and crystalloids.
Objectives: To quantify the effect on mortality of human albumin and plasma protein fraction (PPF) administration in the management of critically ill patients.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Injuries Group Specialised Register (searched 31 May 2011), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2011, Issue 2), MEDLINE (Ovid) (1948 to week 3 May 2011), EMBASE (Ovid) (1980 to Week 21 2011), CINAHL (EBSCO) (1982 to May 2011), ISI Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) (1970 to May 2011), ISI Web of Science: Conference Proceedings Citation Index - Science (CPCI-S) (1990 to May 2011), PubMed (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez/) (searched 10 June 2011, limit: last 60 days). Reference lists of trials and review articles were checked, and authors of identified trials were contacted.
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials comparing albumin or PPF with no albumin or PPF or with a crystalloid solution in critically ill patients with hypovolaemia, burns or hypoalbuminaemia.
Data collection and analysis: We collected data on the participants, albumin solution used, mortality at the end of follow up, and quality of allocation concealment. Analysis was stratified according to patient type.
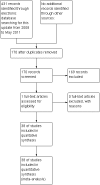
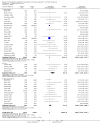
Main results: We found 38 trials meeting the inclusion criteria and reporting death as an outcome. There were 1,958 deaths among 10,842 trial participants.For hypovolaemia, the relative risk of death following albumin administration was 1.02 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.92 to 1.13). This estimate was heavily influenced by the results of the SAFE trial, which contributed 75.2% of the information (based on the weights in the meta-analysis). For burns, the relative risk was 2.93 (95% CI 1.28 to 6.72) and for hypoalbuminaemia the relative risk was 1.26 (95% CI 0.84 to 1.88). There was no substantial heterogeneity between the trials in the various categories (Chi(2) = 26.66, df = 31, P = 0.69). The pooled relative risk of death with albumin administration was 1.05 (95% CI 0.95 to 1.16).
Authors' conclusions: For patients with hypovolaemia, there is no evidence that albumin reduces mortality when compared with cheaper alternatives such as saline. There is no evidence that albumin reduces mortality in critically ill patients with burns and hypoalbuminaemia. The possibility that there may be highly selected populations of critically ill patients in which albumin may be indicated remains open to question. However, in view of the absence of evidence of a mortality benefit from albumin and the increased cost of albumin compared to alternatives such as saline, it would seem reasonable that albumin should only be used within the context of well concealed and adequately powered randomised controlled trials.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
Update of
-
Human albumin solution for resuscitation and volume expansion in critically ill patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;(10):CD001208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001208.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Nov 09;(11):CD001208. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001208.pub4. PMID: 21975732 Updated.
Comment in
-
[Is the use of human albumin for volume expansion justified?].Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013 Jan;138(1-2):14. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1329136. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2013. PMID: 23250687 German. No abstract available.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bland 1973 {published data only}
Bland 1976 {published data only}
-
- Bland RD, Clarke TL, Harden LB. Rapid infusion of sodium bicarbonate and albumin into high‐risk premature infants soon after birth: A controlled, prospective trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1976;124:263‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boldt 1993 {published data only}
-
- Boldt J, Knothe C, Zickmann B, Andres P, Dapper F, Hempelmann G. Influence of different intravascular volume therapies on platelet function in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1993;76:1185‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boutros 1979 {published data only}
-
- Boutros AR, Ruess R, Olson L, Hoyt JL, Baker WH. Comparison of hemodynamic, pulmonary, and renal effects of use of three types of fluids after major surgical procedures on the abdominal aorta. Critical Care Medicine 1979;7(1):9‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Brown 1988 {published data only}
-
- Brown RO, Bradley JE, Bekemeyer WB, Luther RW. Effect of albumin supplementation during parenteral nutrition on hospital morbidity. Critical Care Medicine 1988;16:1177‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cooper 2006 {published data only}
-
- Cooper AB, Cohn SM, Zhang HBS, Hanna K, Stewart TE, Slutsky AS. Five percent albumin for adult burn shock resuscitation: Lack of effect on daily multiple organ dysfunction score. Transfusion 2006;46(1):80‐9. - PubMed
Dubois 2006 {published data only}
-
- Dubois M J, Orellana‐Jimenez C, Melot C, Backer D, Berre J, Leeman M, et al. Albumin administration improves organ function in critically ill hypoalbuminemic patients: A prospective, randomized, controlled, pilot study.[see comment]. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34(10):2536‐40. - PubMed
Ernest 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ernest D, Belzberg AS, Dodek PM. Distribution of normal saline and 5% albumin infusions in septic patients. Critical Care Medicine 1999;27(1):46‐50. - PubMed
Ernest 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ernest D, Belzberg AS, Dodek PM. Distribution of normal saline and 5% albumin infusions in cardiac surgical patients. Critical Care Medicine 2001;29(19):2299‐302. - PubMed
Foley 1990 {published data only}
-
- Foley EF, Borlase BC, Dzik WH, Bistrian BR, Benotti PN. Albumin supplementation in the critically ill: a prospective randomised trial. Archives of Surgery 1990;125:739‐42. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gallagher 1985 {published data only}
-
- Gallagher JD, Moore RA, Kerns D, Jose AB, Botros SB, Flicker S, et al. Effects of colloid or crystalloid administration on pulmonary extravascular water in the postoperative period after coronary artery bypass grafting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1985;64:753‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Golub 1994 {published data only}
-
- Golub R, Sorrento JJ Jr, Cantu R Jr, Nierman DM, Moideen A, Stein HD. Efficacy of albumin supplementation in the surgical intensive care unit: a prospective, randomized study. Critical Care Medicine 1994;22(4):613‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Goodwin 1983 {published data only}
Greenhalgh 1995 {published data only}
-
- Greenhalgh DG, Housinger TA, Kagan RJ, et al. Maintenance of serum albumin levels in pediatric burn patients: a prospective, randomized trial. Journal of Trauma 1995;39(1):67‐73; discussion 73‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Greenough 1993 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Greenough A, Emery E, Hird MF, Gamsu HR. Randomised controlled trial of albumin infusion in ill preterm infants. European Journal of Pediatrics 1993;152:157‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Grundmann 1982 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann R, Meyer H. The significance of colloid osmotic pressure measurement after crystalloid and colloid infusions. Intensive Care Medicine 1982;8:179‐86. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jelenko 1978 {published data only}
-
- Jelenko C 3rd. Fluid therapy and the HALFD method. Journal of Trauma 1979;19 Suppl(11):866‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jelenko C 3rd, Solenberger RI, Wheeler ML, Callaway BD. Shock and resuscitation. III. Accurate refractometric COP determinations in hypovolemia treated with HALFD. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians 1979;8(7):253‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jelenko C 3rd, Wheeler ML, Callaway BD, Divilio LT, Bucklen KR, Holdredge TD. Shock and resuscitation. II: volume repletion with minimal edema using the "HALFD" (Hypertonic Albuminated Fluid Demand) regimen. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians 1978;7(9):326‐33. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Jelenko C 3rd, Williams JB, Wheeler ML, et al. Studies in shock and resuscitation, I: use of a hypertonic, albumin‐containing, fluid demand regimen (HALFD) in resuscitation. Critical Care Medicine 1979;7(4):157‐67. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kanarek 1992 {published data only}
-
- Kanarek KS, Williams PR, Blair C. Concurrent administration of albumin with total parenteral nutrition in sick newborn infants. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 1992;16:49‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lowe 1977 {published data only}
-
- Lowe RJ, Moss GS, Jilek J, Levine HD. Crystalloid versus colloid in the etiology of pulmonary failure after trauma ‐ a randomized trial in man. Critical Care Medicine 1979;7(3):107‐12. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lowe RJ, Moss GS, Jilek J, Levine HD. Crystalloid vs colloid in the etiology of pulmonary failure after trauma: a randomized trial in man. Surgery 1977;1(6):676‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Moss GS, Lowe RJ, Jilek J, Levine HD. Colloid or crystalloid in the resuscitation of hemorrhagic shock: a controlled clinical trial. Surgery 1981;89(4):434‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lucas 1978 {published data only}
-
- Clift DR, Lucas CE, Ledgerwood AM, Sardesai V, Kithier K, Grabow D. The effect of albumin resuscitation for schock on the immune response to tetanus toxoid. Journal of Surgical Research 1982;32:449‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Johnson SD, Lucas CE, Gerrick SJ, Ledgerwood AM, Higgins. Altered coagulation after albumin supplements for treatment of oligaemic shock. Archives of Surgery 1979;114:379‐83. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lucas CE, Bouwman DL, Ledgerwood AM, Higgins R. Differential serum protein changes following supplemental albumin resuscitation for hypovolaemic shock. Journal of Trauma 1980;20(1):47‐51. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Lucas CE, Weaver D, Higgins RF, Ledgerwood AM, Johnson SD, Bouwman DL. Effects of albumin versus non‐albumin resuscitation on plasma volume and renal excretory function. Journal of Trauma 1978;18:565‐70. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Weaver DW, Ledgerwood AM, Lucas CE, Higgins R, Bouwman DL, Johnson SD. Pulmonary effects of albumin resuscitation for severe hypovolaemic shock. Archives of Surgery 1978;113:387‐92. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Maitland 2005 {published data only}
-
- Maitland K, Pamba A, English M, Peshu N, Levin M, Marsh K, et al. Pre‐transfusion management of children with severe malarial anaemia: a randomised controlled trial of intravascular volume expansion. British Journal of Haematology 2005;128(3):393‐400. - PubMed
Maitland 2011 {published data only}
-
- Maitland K, Kiguli S, Opoka RO, Engoru C, Olupot‐Olupot P, Akech SO, et al. Mortality after fluid bolus in African children with severe infection. New England Journal of Medicine 2011:(Electronic). 0028‐4793 (Linking). - PubMed
McNulty 1993 {published data only}
-
- McNulty SE, Sharkey SJ, Asam B, Lee JH. Evaluation of STAT‐CRIT Hematocrit Determination in comparison to Coulter and Centrifuge: the effects of isotonic hemodilution and albumin administration. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1993;76:830‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Myburgh 2007 {published data only}
-
- Myburgh J, Cooper J, Finfer S, Bellomo R, Norton R, Bishop N, et al. Saline or Albumin for Fluid Resuscitation in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury. New England Journal of Medicine 2007;357(9):874‐84. - PubMed
Nielsen 1985 {published data only}
-
- Nielsen OM, Engell HC. Effects of maintaining normal plasma colloid osmotic pressure on renal function and excretion of sodium and water after major surgery: a randomised study. Danish Medical Bulletin 1985;32:182‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nielsen OM, Engell HC. Extracellular fluid volume and distribution in relation to changes in plasma colloid osmotic pressure after major surgery. A randomised study. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1985;151:221‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nielsen OM, Thunedborg P, Jorgensen K. Albumin administration and acute phase proteins in abdominal vascular surgery: a randomised study. Danish Medical Bulletin 1989;36:496‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nilsson 1980 {published data only}
-
- Nilson E, Lamke O, Liljedahl SO, Elfstrom K. Is albumin therapy worthwhile in surgery for colorectal cancer?. Acta Chirurgica Scandinavica 1980;146:619‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oca 1999 {published data only}
-
- Oca MJ, Nelson M, Donn SM. Randomized trial of normal saline (NS) versus 5% albumin (ALB) for the treatment of neonatal hypotension. Pediatric Research. 1999; Vol. 45:#1265. - PubMed
Oca 2003 {published data only}
-
- Oca MJ, Nelson M, Donn SM. Randomized trial of normal saline versus 5% albumin for the treatment of neonatal hypotension. Journal of Perinatology 2003;23(6):473‐6. - PubMed
Pockaj 1994 {published data only}
-
- Pockaj BA, Yang JC, Lotze MT, et al. A prospective randomized trial evaluating colloid versus crystalloid resuscitation in the treatment of the vascular leak syndrome associated with interleukin‐2 therapy. Journal of Immunotherapy 1994;15(1):22‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Prien 1990 {published data only}
-
- Prien T, Backhaus N, Pelster F, Pircher W, Bunte H, Lawin P. Effect of intraoperative fluid administration and colloid osmotic pressure on the formation of intestinal edema during gastrointestinal surgery. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 1990;2:317‐23. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Quinlan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Quinlan GJ, Mumby S, Martin GS, Bernard GR, Gutteridge JM, Evans TW. Albumin influences total plasma antioxidant capacity favorably in patients with acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32(3):755‐9. - PubMed
Rackow 1983 {published data only}
-
- Rackow EC, Falk JL, Fein IA, et al. Fluid resuscitation in circulatory shock: a comparison of the cardiorespiratory effects of albumin, hetastarch, and saline solutions in patients with hypovolemic and septic shock. Critical Care Medicine 1983;11(11):839‐50. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Rubin 1997 {published data only}
-
- Rubin H, Carlson S, DeMeo M, Ganger D, Craig R. Randomized, double‐blind study of intravenous human albumin in hypoalbuminemic patients receiving total parenteral nutrition. Critical Care Medicine 1997;25:249‐52. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
SAFE 2004 {published data only}
-
- The SAFE Study Investigators. A comparison of albumin and saline for fluid resuscitation in the intensive care unit. New England Journal of Medicine 2004;350:2247‐56. - PubMed
Shah 1977 {published data only}
-
- Shah DM, Broner BD, Dutton RE, Newell JC, Powers SR. Cardiac output and pulmonary wedge pressure. Use for evaluation of fluid replacement in trauma patients. Archives of Surgery 1977;112:1161‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Skillman 1975 {published data only}
-
- Skillman JJ, Restall DS, Salzman EW. Randomized trial of albumin vs. electrolyte solutions during abdominal aortic operations. Surgery 1975;78(3):291‐303. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
So 1997 {published data only}
Tollofsrud 1995 {published data only}
-
- Svennevig JL, Tollofsrud S, Kongsgaard U, Noddeland H, Mohr B, Ozer M, Mollnes TE. Complement activation during and after open‐heart surgery is only marginally affected by the choice of fluid for volume replacement. Perfusion 1996;11:326‐32. - PubMed
-
- Tollofsrud S, Svennevig JL, Breivik H, et al. Fluid balance and pulmonary functions during and after coronary artery bypass surgery: Ringer’s acetate compared with dextran, polygeline, or albumin. Acta Anaesthsiologica Scandinavica 1995;39:671‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Virgilio 1979 {published data only}
-
- Virgilio RW, Rice CL, Smith DE, et al. Crystalloid vs. colloid resuscitation: is one better? A randomized clinical study. Surgery 1979;85(2):129‐39. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Woittiez 1998 {unpublished data only}
-
- Timmer B, Hondebrink Y, Oude Nijhuis J, Woittiez AJJ. Restoration of colloid osmotic pressure in hypoalbuminaemic patients. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 1998;52:A42.
-
- Woittiez AJ. Restoration of colloid osmotic pressure in post operative intensive care patients. A randomised placebo controlled trial with albumin 20% and hydroxy‐ethyl starch. In: Medical Editors' Trial Amnesty. In: The Cochrane Controlled Trials Register In: The Cochrane Library, Issue 2, 1998. Oxford: Update Software.
Wojtysiak 1992 {published data only}
-
- Binkley JF, Brown RO, Wojtysiak SL, Powers DA, Kudsk KA. Effects of human albumin administration on visceral protein markers in patients receiving parenteral nutrition. Clinical Pharmacy 1993;12:377‐9. - PubMed
-
- Wojtysiak SL, Brown RO, Roberson D, Powers DA, Kudsk KA. Effect of hypoalbuminaemia and parenteral nutrition on free water excretion and electrolyte‐free water resorption. Critical Care Medicine 1992;20:164‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Woods 1993 {published data only}
-
- Woods MS, Kelley H. Oncotic pressure, albumin and ileus: the effect of albumin replacement on postoperative ileus. The American Surgeon 1993;59:758‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zetterstrom 1981a {published data only}
-
- Zetterstrom H, Hedstrand U. Albumin treatment following major surgery. I. Effects on plasma oncotic pressure, renal function and peripheral oedema. Acta Anaesthsiologica Scandinavica 1981;25:125‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Zetterstrom 1981b {published data only}
-
- Zetterstrom H. Albumin treatment following major surgery. II. Effects on postoperative lung function and circulatory adaptation. Acta Anaesthsiologica Scandinavica 1981;25:133‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Artru 1989 {published data only}
-
- Artru F, Philippon B, Flachaire E, et al. A controlled study of Dextran 40: effect on cerebral blood flow and metabolic rates in acute head trauma. Intensive Care Medicine 1989;15(8):499‐504. - PubMed
Bellomo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Bellomo R, Morimatsu H, French C, Cole L, Story D, Uchino S, et al. The effects of saline or albumin resuscitation on acid‐base status and serum electrolytes. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34(12):2891‐7. - PubMed
Brehme 1993 {published data only}
-
- Brehme S, Keysser G, Turowski A, Schmidt HH. Hemorheologic effects of hydroxyethyl starch 200/0.5, dextran 40, oxypolygelatine and full electrolyte solution over 48 hours. Zeitschrift fur die gesamte innere Medizinund ihre Grenzgebiete 1993;48(10):506‐10. - PubMed
Carlon 1979 {published data only}
-
- Carlon GC, Kahn RC, Bertoni G, Campfield PB, Howland WS, Goldiner PL. Rapid volume expansion in patients with interstitial lung diseases. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1979;58:13‐8. - PubMed
Fiorica 1991 {published data only}
-
- Fiorica JV, Roberts WS, Hoffman MS, Barton DP, Finan MA, Lyman G, Cavanagh D. Concentrated albumin infusion as an aid to postoperative recovery after pelvic exenteration. Gynecologic Oncology 1991;43:265‐9. - PubMed
Goslinga 1992 {published data only}
-
- Goslinga H, Eijzenbach V, Heuvelmans JH, et al. Custom‐tailored hemodilution with albumin and crystalloids in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 1992;23(2):181‐8. - PubMed
-
- Goslinga H, Eijzenbach V, Heuvelmans JH, Nes JC, Kurk RM, Bezemer PD. Individualized hemodilution in acute brain infarct using a 20% albumin solution and physiological saline solution. Ned Nederlands Tijdschrift voor Geneeskunde 1992;136(49):2422‐8. - PubMed
-
- Goslinga H, Heuvelmans JH, Schmid Schonbein H. Hemodilution and rehydration in acute ischemic stroke. A preliminary report on the Amsterdam Stroke Study. Acta Medica Austriaca 1991;18 Suppl 1:41‐4. - PubMed
Grundmann 1985 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann R, Heistermann S. Postoperative albumin infusion therapy based on colloid osmotic pressure. Archives of Surgery 1985;120:911‐5. - PubMed
Grundmann 1986 {published data only}
-
- Grundmann R, Lehndorff C. Indications for postoperative human albumin therapy in the intensive care unit: a prospective randomised study. Langenbecks Archiv fur Chirurgie 1986;367:235‐46. - PubMed
Hauser 1980 {published data only}
-
- Hauser CJ, Shoemaker WC, Turpin I, Goldberg SJ. Oxygen transport respons to colloids and crystalloids in critically ill surgical patients. Surgery 1980;150(6):811‐6. - PubMed
Lagonidis 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lagonidis D, Magder S. Acute volume loading with colloid vs. crystalloid after coronary artery bypass. Intensive Care Medicine 1992;18 Suppl 2:225.
Lennihan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lennihan L, Mayer SA, Fink ME, Beckford A, Paik MC, Zhang H, et al. Effect of hypervolemic therapy on cerebral blood flow after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 2000;31(2):383‐91. - PubMed
Magder 1999 {published data only}
-
- Magder S, Lagonidis D. Effectiveness of albumin versus normal saline as a test of volume responsiveness in post‐cardiac surgery patients. Journal of Critical Care 1999;14(4):164‐71. - PubMed
Maitland 2005a {published data only}
-
- Maitland K, Pamba A, English M, Peshu N, Marsh K, Newton C, et al. Randomized trial of volume expansion with albumin or saline in children with severe malaria: Preliminary evidence of albumin benefit. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2005;40(4):538‐45. - PubMed
Martin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Martin GS, Mangialardi RJ, Wheeler AP, Berhard GR. Albumin and diuertics in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 1999;159(3):A376.
Metildi 1984 {published data only}
-
- Metildi LA, Shackford SR, Virgilio RW, Peters RM. Crystalloid versus colloid in fluid resuscitation of patients with severe pulmonary insufficiency. Surgical Gynecology and Obstetrics 1984;158(3):207‐12. - PubMed
Steinberg 1989 {published data only}
-
- Steinberg B, Kochs E, Bause H, Schulte am Esch J. Effects of low molecular weight hydroxyethyl starch (HES 40) in comparison with Ringer solution on oxygen tension in skeletal muscles of infected patients. Anasthesie Intensivtherapie Notfallmedizin 1989;24(6):377‐81. - PubMed
Tomita 1994 {published data only}
-
- Tomita H, Ito U, Tone O, Masaoka H, Tominaga B. High colloid oncotic therapy for contusional brain edema. Acta Neurochirurgica 1994;Suppl:547‐9. - PubMed
Additional references
ABPI 1998
-
- ABPI Compendium of data sheets and summaries of produce characteristics 1998‐99. Association of the British Pharmaceutical Industry, London 1998.
Boldt 2009
-
- Boldt J, Suttner S, Brosch C, Lehmann A, Roehm K, Mengitsu A. Cardiopulminary bypass priming using a high dose of a balanced hydroxyethyl starch versus an albumin‐based priming strategy. Anesthesia & Analgesia 2009;109:1752‐62. - PubMed
Goldwasser 1997
-
- Goldwasser P, Feldman J. Association of serum albumin and mortality risk. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1997;50(6):693‐703. - PubMed
Reinhart 2011
-
- Reinhart K, Takala J. Hydroxyethyl Starches: What Do We Still Know?. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(3):507‐11. - PubMed
Shafer 2011
-
- Shafer SL. Shadow of Doubt. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(3):498‐500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous