Antidepressants for pain management in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 22071859
- PMCID: PMC12214451
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008920.pub2
Antidepressants for pain management in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Pain management is a high priority for patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Antidepressants are sometimes used as adjuvant agents to enhance pain relief, help with sleep and reduce depression. Such antidepressants include tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), selective serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs). However, the prescription of antidepressants in this population remains controversial because of conflicting scientific evidence.
Objectives: The aim of this review was to determine the efficacy and safety of antidepressants in pain management in patients with RA.
Search methods: We performed a computer assisted search of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2010, 4th quarter); MEDLINE (1950 to November Week 1, 2010); EMBASE (2010 Week 44); and PsycINFO (1806 to November Week 2, 2010). We also searched the 2008-2009 American College of Rheumatology (ACR) and European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) abstracts and performed a handsearch of reference lists of articles.
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) which compared an antidepressant therapy to another therapy (active or placebo, including non-pharmacological therapies) in adult patients with RA who had at least one clinically relevant outcome measure. Outcomes of interest were pain, adverse effects, function, sleep, depression and quality of life.
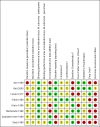
Data collection and analysis: Two blinded review authors independently extracted data and assessed the risk of bias in the trials. We conducted meta-analyses to examine the efficacy of antidepressants on pain, depression and function, as well as their safety.
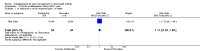
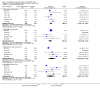
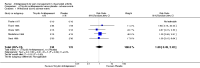
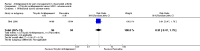
Main results: We included eight RCTs (652 participants) in this review. All trials evaluated TCAs and two trials evaluated a SSRI as a comparator. Seven of the eight trials had high risk of bias. There was insufficient data for a number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome (NNTB) to be calculated for the primary outcome measure of pain. The qualitative analyses found no evidence of an effect of antidepressants on pain intensity or depression in the short-term (less than one week), and conflicting evidence of a medium- (one to six weeks) or long-term (more than six weeks) benefit. There were significantly more minor adverse events in patients receiving TCAs compared with those receiving a placebo (risk ratio (RR) 2.27, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.17 to 4.42), but there was no significant increase in withdrawals due to an adverse event (RR 1.09, 95% CI 0.49 to 2.42).
Authors' conclusions: There is currently insufficient evidence to support the routine prescription of antidepressants as analgesics in patients with RA as no reliable conclusions about their efficacy can be drawn from eight placebo RCTs. The use of these agents may be associated with adverse events which are generally mild and do not lead to cessation of treatment. More high quality trials are needed in this area.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures

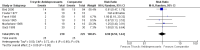
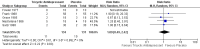



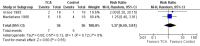






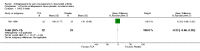
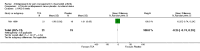
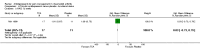


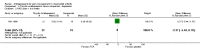
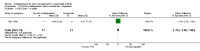
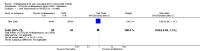
Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008920
References
References to studies included in this review
Ash 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ash G, Dickens CM, Creed FH, Jayson MI, Tomenson B. The effects of dothiepin on subjects with rheumatoid arthritis and depression. Rheumatology 1999;38(10):959‐67. - PubMed
Bird 2000 {published data only}
-
- Bird H, Broggini M. Paroxetine versus amitriptyline for treatment of depression associated with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double blind, parallel group study. Journal of Rheumatology 2000;27(12):2791‐7. - PubMed
Fowler 1977 {published data only}
-
- Fowler PD, MacNeill A, Spencer D, Robinson ET, Dick WC. Imipramine, rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid factor. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1977;5(3):241‐6. - PubMed
Frank 1988 {published data only}
-
- Frank RG, Kashani JH, Parker JC, Beck NC, Brownlee‐Duffeck M, Elliott TR, et al. Antidepressant analgesia in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 1988;15:1632‐8. - PubMed
Grace 1985 {published data only}
-
- Grace EM, Bellamy N, Kassam Y, Buchanan WW. Controlled, double‐blind, randomized trial of amitriptyline in relieving articular pain and tenderness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1985;9(6):426‐9. - PubMed
Macfarlane 1986 {published data only}
-
- Macfarlane JG, Jalali S, Grace EM. Trimipramine in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized double‐blind trial in relieving pain and joint tenderness. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1986;10(2):89‐93. - PubMed
Saarialho‐Kere 1988 {published data only}
-
- Saarialho‐Kere U, Julkunen H, Mattila MJ, Seppälä T. Psychomotor performance of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: cross‐over comparison of dextropropoxyphene, dextropropoxyphene plus amitriptyline, indomethacin, and placebo. Pharmacology & Toxicology 1988;63(4):286‐92. - PubMed
Sarzi 1988 {published data only}
-
- Sarzi Puttini P, Cazzola M, Boccassini L, Ciniselli G, Santandrea S, Caruso I, et al. A comparison of dothiepin versus placebo in the treatment of pain in rheumatoid arthritis and the association of pain with depression. The Journal of International Medical Research 1988;16(5):331‐7. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Gringras 1976 {published data only}
-
- Gringras M. A clinical trial of Tofranil in rheumatic pain in general practice. Journal of International Medical Research 1976;4((2 Suppl)):41‐9. - PubMed
MacNeill 1976 {published data only}
-
- MacNeill AL, Dick WC. Imipramine and rheumatoid factor. Journal of International Medical Research 1976;4(2 Suppl):23‐7. - PubMed
McQuay 1993 {published data only}
-
- McQuay HJ, Carroll D, Glynn CJ. Dose‐response for analgesic effect of amitriptyline in chronic pain. Anaesthesia 1993;48(4):281–5. - PubMed
Parker 2003 {published data only}
-
- Parker JC, Smarr KL, Slaughter JR, Johnston SK, Priesmeyer ML, Hanson KD, et al. Management of depression in rheumatoid arthritis: a combined pharmacologic and cognitive‐behavioral approach. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2003;49(6):766‐77. - PubMed
Rani 1996 {published data only}
-
- Rani PU, Naidu MU, Prasad VB, Rao TR, Shobha JC. An evaluation of antidepressants in rheumatic pain conditions. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1996;83(2):371‐5. - PubMed
Scott 1969 {published data only}
-
- Scott WA. The relief of pain with an antidepressant in arthritis. Practitioner 1969;202(212):802‐7. - PubMed
Slaughter 2002 {published data only}
-
- Slaughter JR, Parker JC, Martens MP, Smarr KL, Hewett JE. Clinical outcomes following a trial of sertraline in rheumatoid arthritis. Psychosomatics 2002;43(1):36–41. - PubMed
Thorpe 1974 {published data only}
-
- Thorpe P, Marchant‐Williams R. The role of an antidepressant, dibenzepin (Noveril), in the relief of pain in chronic arthritic states. Medical Journal of Australia 1974;1(8):264‐6. - PubMed
Wheatley 1986 {published data only}
-
- Wheatley D. Antidepressants in elderly arthritics. The Practitioner 1986;230(1415):477‐81. [PUBMED: 3529072] - PubMed
Additional references
Baba 2001
Bird 1960
Blackburn‐Munro 2001
-
- Blackburn‐Munro G, Blackburn‐Munro RE. Chronic pain, chronic stress and depression: coincidence or consequence?. Journal of Neuroendocrinology 2001;13(12):1009‐23. - PubMed
Cates 2004
-
- Cates C. Dr Chris Cates' EBM Web Site. Visual Rx Version 3. www.nntonline.net/visualrx/ 2004.
DeAngelis 2004
-
- DeAngelis CD, Drazen JM, Frizelle FA, Haug C, Hoey J, Horton R, et al. Clinical trial registration: a statement from the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. JAMA 2004;292(11):1363‐4. - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta‐analyses. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Dworkin 2008
-
- Dworkin RH, Turk DC, Wyrwich KW, Beaton D, Cleeland CS, Farrar JT, et al. Interpreting the clinical importance of treatment outcomes in chronic pain clinical trials: IMMPACT recommendations. Journal of Pain 2008;9(2):105‐21. - PubMed
Elenkov 2000
-
- Elenkov IJ, Wilder RL, Chrousos GP, Vizi ES. The sympathetic nerve ‐ an integrative interface between two super systems: The brain and the immune system. Pharmacological Reviews 2000;52(4):595‐638. - PubMed
Eschalier 1999
-
- Eschalier A, Ardid D, Dubray C. Tricyclic and other antidepressants as analgesics. In: Sawynok J, Cowan A editor(s). Novel aspects of pain management: opioids and beyond. New York: Wiley, 1999.
Fries 1980
-
- Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG, Holman HR. Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1980;23(2):137‐45. - PubMed
Furukawa 2002
Gill 2002
Hauser 2009
-
- Hauser W, Bernardy K, Uceyler N, Sommer C. Treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome with antidepressants: a meta‐analysis. JAMA 2009;301(2):198‐209. - PubMed
Heiberg 2002
-
- Heiberg T, Kvien TK. Preferences for improved health examined in 1,024 patients with rheumatoid arthritis: pain has highest priority. Arthritis and Rheumatism 2002;47(4):391‐7. - PubMed
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC (editors). Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (editors). Chapter 16: Special topics in statistics. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Julius 2001
-
- Julius D, Basbaum AI. Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 2001;413(6852):203–10. - PubMed
Kubera 2001
-
- Kubera M, Lin AH, Kenis G, Bosmans E, Bockstaele D, Maes M. Anti‐Inflammatory effects of antidepressants through suppression of the interferon‐gamma/interleukin‐10 production ratio. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology 2001;21(2):199‐206. - PubMed
Kuipers 1962
-
- Kuipers RK. Imipramine in the treatment of rheumatic patients. Acta Rheumatologica Scandinavica 1962;8:45‐51. - PubMed
Kvien 2004
-
- Kvien TK. Epidemiology and burden of illness of rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacoeconomics 2004;22(2 Suppl 1):1‐12. - PubMed
Lynch 2001
Magni 1993
-
- Magni G, Marchetti M, Moreschi C, Merskey H, Luchini SR. Chronic musculoskeletal pain and depressive symptoms in the National Health and Nutrition Examination. I. Epidemiologic follow‐up study. Pain 1993;53(2):163‐8. - PubMed
Marchand 2005
-
- Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB. Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nature Neuroscience 2005;6(7):521–32. - PubMed
Marino 1999
-
- Marino F, Cosentino M, Bombelli R, Ferrari M, Lecchini S, Frigo G. Endogenous catecholamine synthesis, metabolism storage, and uptake inhuman peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Experimental Hematology 1999;27(3):489‐95. - PubMed
Minnock 2003
-
- Minnock P, FitzGerald O, Bresnihan B. Women with established rheumatoid arthritis perceive pain as the predominant impairment of health status. Rheumatology 2003;42(8):995‐1000. - PubMed
Moore 2010
-
- Moore RA, Eccleston C, Derry S, Wiffen P, Bell RF, Straube S, et al. "Evidence" in chronic pain‐ establishing best practice in the reporting of systematic reviews. Pain 2010;150(3):386‐9. - PubMed
Morin 1998
-
- Morin CM, Gibson D, Wade J. Self‐reported sleep and mood disturbance in chronic pain patients. Clinical Journal of Pain 1998;14(4):311‐4. - PubMed
Onghena 1992
-
- Onghena P, Houdenhove B. Antidepressant‐induced analgesia in chronic non‐malignant pain: a meta‐analysis of 39 placebo‐controlled studies. Pain 1992;49(2):205–19. - PubMed
Perrot 2006
-
- Perrot S, Maheu E, Javier RM, Eschalier A, Coutaux A, LeBars M, et al. Guidelines for the use of antidepressants in painful rheumatic conditions. European Journal of Pain 2006;10(3):185–92. - PubMed
Perrot 2008
-
- Perrot S, Javier RM, Marty M, Jeunne C, Laroche F, CEDR (Cercle d'Etude de la Douleur en Rhumatologie France). Is there any evidence to support the use of anti‐depressants in painful rheumatological conditions? Systematic review of pharmacological and clinical studies. Rheumatology 2008;47(8):1117–23. - PubMed
Pincus 1983
-
- Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1983;26(11):1346‐53. - PubMed
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.1. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Saarto 2007
Sawynok 2001
Scholz 2005
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and ‘Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Skevington 1998
-
- Skevington SM. Investigating the relationship between pain and discomfort and quality of life, using the WHOQOL. Pain 1998;76(3):395–406. - PubMed
Sterne 2011
-
- Sterne JAC, Egger M, Moher D (editors). Chapter 10: Addressing reporting biases. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Intervention. Version 5.1 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Watson 1994
-
- Watson CP. Antidepressant drugs as adjuvant analgesics. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management 1994;9(6):392‐405. - PubMed
Woolf 1999
Woolf 2000
-
- Woolf CJ, Salter MW. Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science 2000;288(5472):1765–9. - PubMed
Yaron 1999
-
- Yaron I, Shirazi I, Judovich R, Levartovsky D, Caspi D, Yaron M. Fluoxetineand amitriptyline inhibit nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and hyaluronic acid production in human synovial cells and synovial tissue cultures. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1999;42(12):2561–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

