Segregation and pathfinding of callosal axons through EphA3 signaling
- PMID: 22072676
- PMCID: PMC6633229
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3303-11.2011
Segregation and pathfinding of callosal axons through EphA3 signaling
Abstract
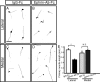
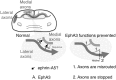
The corpus callosum, composed of callosal axons, is the largest structure among commissural connections in eutherian animals. Axon pathfinding of callosal neurons has been shown to be guided by intermediate targets, such as midline glial structures. However, it has not yet been understood completely how axon-axon interactions, another major mechanism for axon pathfinding, are involved in the pathfinding of callosal neurons. Here, we show that callosal axons from the medial and lateral regions of the mouse cerebral cortex pass through the dorsal and ventral parts, respectively, of the corpus callosum. Using an explant culture system, we observed that the axons from the medial and lateral cortices were segregated from each other in vitro, and that this segregation was attenuated by inhibition of EphA3 signaling. We also found that knockdown of EphA3, which is preferentially expressed in the lateral cortex, resulted in disorganized segregation of the callosal axons and disrupted axon pathfinding in vivo. These results together suggest the role of axonal segregation in the corpus callosum, mediated at least in part by EphA3, in correct pathfinding of callosal neurons.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Axon guidance mechanisms for establishment of callosal connections.Neural Plast. 2013;2013:149060. doi: 10.1155/2013/149060. Epub 2013 Feb 24. Neural Plast. 2013. PMID: 23533817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cascade of morphogenic signaling initiated by the meninges controls corpus callosum formation.Neuron. 2012 Feb 23;73(4):698-712. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.11.036. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 22365545 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neuronal activity supports the axon development of callosal projection neurons during different post-natal periods in the mouse cerebral cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2010 Feb;31(3):410-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.07070.x. Epub 2010 Jan 25. Eur J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20105242
-
Timing and origin of the first cortical axons to project through the corpus callosum and the subsequent emergence of callosal projection cells in mouse.J Comp Neurol. 1998 Oct 19;400(2):197-206. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19981019)400:2<197::aid-cne3>3.0.co;2-4. J Comp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9766399
-
Activity-dependent callosal axon projections in neonatal mouse cerebral cortex.Neural Plast. 2012;2012:797295. doi: 10.1155/2012/797295. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Neural Plast. 2012. PMID: 23213574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NeuroGT: A brain atlas of neurogenic tagging CreER drivers for birthdate-based classification and manipulation of mouse neurons.Cell Rep Methods. 2021 May 25;1(3):100012. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2021.100012. eCollection 2021 Jul 26. Cell Rep Methods. 2021. PMID: 35474959 Free PMC article.
-
Callosal responses in a retrosplenial column.Brain Struct Funct. 2018 Apr;223(3):1051-1069. doi: 10.1007/s00429-017-1529-5. Epub 2017 Oct 28. Brain Struct Funct. 2018. PMID: 29081006 Free PMC article.
-
SeeDB: a simple and morphology-preserving optical clearing agent for neuronal circuit reconstruction.Nat Neurosci. 2013 Aug;16(8):1154-61. doi: 10.1038/nn.3447. Epub 2013 Jun 23. Nat Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23792946
-
Axon position within the corpus callosum determines contralateral cortical projection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jul 16;110(29):E2714-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1310233110. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23812756 Free PMC article.
-
Mef2c Controls Postnatal Callosal Axon Targeting by Regulating Sensitivity to Ephrin Repulsion.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 22:2025.01.22.634300. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.22.634300. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Neurosci. 2025 May 21;45(21):e0201252025. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0201-25.2025. PMID: 39896513 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Chan SO, Chung KY. Changes in axon arrangement in the retinofugal [correction of retinofungal] pathway of mouse embryos: confocal microscopy study using single- and double-dye label. J Comp Neurol. 1999;406:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Dufour A, Seibt J, Passante L, Depaepe V, Ciossek T, Frisén J, Kullander K, Flanagan JG, Polleux F, Vanderhaeghen P. Area specificity and topography of thalamocortical projections are controlled by ephrin/Eph genes. Neuron. 2003;39:453–465. - PubMed
-
- Egea J, Klein R. Bidirectional Eph-ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007;17:230–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
