Concurrent exposure to methamphetamine and sexual behavior enhances subsequent drug reward and causes compulsive sexual behavior in male rats
- PMID: 22072697
- PMCID: PMC6633219
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4013-11.2011
Concurrent exposure to methamphetamine and sexual behavior enhances subsequent drug reward and causes compulsive sexual behavior in male rats
Abstract
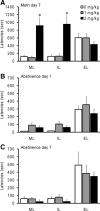
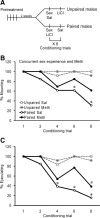
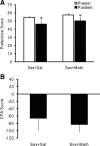
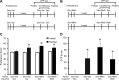
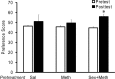
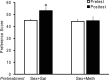
Methamphetamine (Meth) users report having heightened sexual pleasure, numerous sexual partners, and engaging in unprotected sex due to loss of inhibitory control. This compulsive sexual behavior contributes to increased prevalence of sexually transmitted infections, but the neural basis for this is unknown. We previously established a paradigm for compulsive sexual behavior in male rats in which visceral illness induced by lithium chloride was paired with sexual behavior (Davis et al., 2010; Frohmader et al., 2010a). The current study examined the effects of repeated Meth administration on sexual performance, compulsive sexual behavior, and sex or Meth reward. First, results demonstrated that seven daily administrations of 2 mg/kg, but not 1 mg/kg, Meth increased latencies to initiate mating. This impairment was evident 30 min after last Meth administration, but dissipated after 1 or 7 d of subsequent drug abstinence. Repeated 1 mg/kg Meth exposure resulted in compulsive sex-seeking behavior 2 weeks following last Meth administration. This effect was dependent on Meth administration being concurrent with sexual experience and was not observed in sexually experienced animals that received Meth alone. Moreover, concurrent Meth and sexual experience enhanced conditioned place preference (CPP) for Meth, and for concurrent Meth and mating compared with Meth or mating alone. In contrast, CPP for mating alone was decreased. Together, these data indicate that the association between drug use and mating may be required for expression of compulsive sexual behavior and is correlated with increased reward seeking for concurrent Meth exposure and mating.
Figures


References
-
- Agmo A. Copulation-contingent aversive conditioning and sexual incentive motivation in male rats: evidence for a two-stage process of sexual behavior. Physiol Behav. 2002;77:425–435. - PubMed
-
- Agmo A, Berenfeld R. Reinforcing properties of ejaculation in the male rat: role of opioids and dopamine. Behav Neurosci. 1990;104:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft J. Sexual behavior that is “out of control”: a theoretical conceptual approach. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2008;31:593–601. - PubMed
-
- Belcher AM, Feinstein EM, O'Dell SJ, Marshall JF. Methamphetamine influences on recognition memory: comparison of escalating and single-day dosing regimens. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2008;33:1453–1463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
