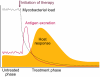
Simple rapid near-patient diagnostics for tuberculosis remain elusive--is a "treat-to-test" strategy more realistic?
- PMID: 22072958
- PMCID: PMC3207897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002207
Simple rapid near-patient diagnostics for tuberculosis remain elusive--is a "treat-to-test" strategy more realistic?
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Steingart KR, Henry M, Laal S, Hopewell PC, Ramsay A, et al. Commercial serological antibody detection tests for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: a systematic review. PLoS Med. 2007;4:e202. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040202. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dheda K, Davids V, Lenders L, Roberts T, Meldau R, et al. Clinical utility of a commercial LAM-ELISA assay for TB diagnosis in HIV-infected patients using urine and sputum samples. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e9848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009848. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McNerney R, Daley P. Towards a point-of-care test for active tuberculosis: obstacles and opportunities. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9:204–213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical