New tetromycin derivatives with anti-trypanosomal and protease inhibitory activities
- PMID: 22072992
- PMCID: PMC3210601
- DOI: 10.3390/md9101682
New tetromycin derivatives with anti-trypanosomal and protease inhibitory activities
Abstract
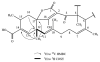
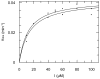
Four new tetromycin derivatives, tetromycins 1-4 and a previously known one, tetromycin B (5) were isolated from Streptomyces axinellae Pol001(T) cultivated from the Mediterranean sponge Axinella polypoides. Structures were assigned using extensive 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy as well as HRESIMS analysis. The compounds were tested for antiparasitic activities against Leishmania major and Trypanosoma brucei, and for protease inhibition against several cysteine proteases such as falcipain, rhodesain, cathepsin L, cathepsin B, and viral proteases SARS-CoV M(pro), and PL(pro). The compounds showed antiparasitic activities against T. brucei and time-dependent inhibition of cathepsin L-like proteases with K(i) values in the low micromolar range.
Keywords: Streptomyces axinellae; anti-trypanosomal; marine sponge; protease inhibition; tetromycin.
Figures







References
-
- Peiris JS, Yuen KY, Osterhaus AD, Stohr K. The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;349:243–2441. - PubMed
-
- Anand K, Ziebuhr J, Wadhwani P, Mesters JR, Hilgenfeld R. Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: Basis for design of anti-SARS drugs. Science. 2003;300:1763–1767. - PubMed
-
- Laport MS, Santos OS, Muricy G. Marine sponges: Potential sources of new antimicrobial drugs. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2009;10:86–105. - PubMed
-
- Scheuermayer M, Pimentel-Elardo S, Fieseler L, Grozdanov L, Hentschel U. Microorganisms of Sponges: Phylogenetic Diversity and Biotechnological Potential. In: Proksch P, Müller WEG, editors. Frontiers in Marine Biotechnology. Horizon Bioscience; Norwich, UK: 2006. pp. 289–312.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

