Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health
- PMID: 22072997
- PMCID: PMC3210606
- DOI: 10.3390/md9101806
Fucoxanthin, a marine carotenoid present in brown seaweeds and diatoms: metabolism and bioactivities relevant to human health
Abstract
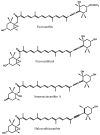
The marine carotenoid fucoxanthin can be found in marine brown seaweeds, the macroalgae, and diatoms, the microalgae, and has remarkable biological properties. Numerous studies have shown that fucoxanthin has considerable potential and promising applications in human health. In this article, we review the current available scientific literature regarding the metabolism, safety, and bioactivities of fucoxanthin, including its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-obese, antidiabetic, antiangiogenic and antimalarial activities, and its protective effects on the liver, blood vessels of the brain, bones, skin, and eyes. Although some studies have shown the bioavailability of fucoxanthin in brown seaweeds to be low in humans, many studies have suggested that a dietary combination of fucoxanthin and edible oil or lipid could increase the absorption rate of fucoxanthin, and thus it might be a promising marine drug.
Keywords: bioactivity; brown seaweed; diatom; fucoxanthin; metabolite.
Figures
References
-
- Dembitsky VM, Maoka T. Allenic and cumulenic lipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2007;46:328–375. - PubMed
-
- Nomura T, Kikuchi M, Kubodera A, Kawakami Y. Proton-donative antioxidant activity of fucoxanthin with 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1997;42:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Beppu F, Niwano Y, Tsukui T, Hosokawa M, Miyashita K. Single and repeated oral dose toxicity study of fucoxanthin (FX), a marine carotenoid, in mice. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2009;34:501–510. - PubMed
-
- Willstätter R, Page HJ. Chlorophyll. XXIV. The pigments of the brown algae. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1914;404:237–271.
-
- Englert G, Bjørnland T, Liaaen-Jensen S. 1D and 2D NMR study of some allenic carotenoids of the fucoxanthin series. Magn Reson Chem. 1990;28:519–528.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources