Kinase inhibitors from marine sponges
- PMID: 22073013
- PMCID: PMC3210622
- DOI: 10.3390/md9102131
Kinase inhibitors from marine sponges
Abstract
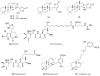
Protein kinases play a critical role in cell regulation and their deregulation is a contributing factor in an increasing list of diseases including cancer. Marine sponges have yielded over 70 novel compounds to date that exhibit significant inhibitory activity towards a range of protein kinases. These compounds, which belong to diverse structural classes, are reviewed herein, and ordered based upon the kinase that they inhibit. Relevant synthetic studies on the marine natural product kinase inhibitors have also been included.
Keywords: anticancer agents; cell regulation; marine natural products; marine sponges; protein kinase inhibitors.
Figures


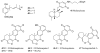

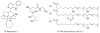
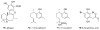
References
-
- Newman DJ, Cragg GM. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007;70:461–477. - PubMed
-
- Faulkner DJ. Marine pharmacology. Antonie Leeuwenhoek. 2000;77:135–145. - PubMed
-
- Haefner B. Drugs from the deep: Marine natural products as drug candidates. Drug Discov. Today. 2003;8:536–544. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Sharma R, Tyagi R. Inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases: Useful targets for cancer treatment. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets. 2008;8:53–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

