Decreasing mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock patients by implementing a sepsis bundle in a hospital setting
- PMID: 22073193
- PMCID: PMC3207817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026790
Decreasing mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock patients by implementing a sepsis bundle in a hospital setting
Abstract
Background: The Surviving Sepsis Campaign (SSC) guidelines for the management of severe sepsis (SS) and septic shock (SSh) have been recommended to reduce morbidity and mortality.
Materials and methods: A quasi-experimental study was conducted in a medical-surgical ICU. Multiple interventions to optimize SS and SSh shock patients' clinical outcomes were performed by applying sepsis bundles (6- and 24-hour) in May 2006. We compared bundle compliance and patient outcomes before (July 2005-April 2006) and after (May 2006-December 2009) implementation of the interventions.
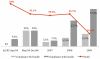
Results: A total of 564 SS and SSh patients were identified. Prior to the intervention, compliance with the 6 hour-sepsis resuscitation bundle was only 6%. After the intervention, compliance was as follows: 8.2% from May to December 2006, 9.3% in 2007, 21.1% in 2008 and 13.7% in 2009. For the 24 hour-management bundle, baseline compliance was 15.0%. After the intervention, compliance was 15.1% from May to December 2006, 21.4% in 2007, 27.8% in 2008 and 44.4% in 2009. The in-hospital mortality was 54.0% from July 2005 to April 2006, 41.1% from May to December 2006, 39.3% in 2007, 41.4% in 2008 and 16.2% in 2009.
Conclusion: These results suggest reducing SS and SSh patient mortality is a complex process that involves multiple performance measures and interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, et al. Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence, outcome, and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Rivers E, Nguyen B, Havstad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1368–1377. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, Gerlach H, Calandra T, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:858–873. - PubMed
-
- Dellinger RP, Carlet JM, Masur H, Gerlach H, Calandra T, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:536–555. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous