Protein replacement therapy partially corrects the cholesterol-storage phenotype in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick type C2 disease
- PMID: 22073306
- PMCID: PMC3207855
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027287
Protein replacement therapy partially corrects the cholesterol-storage phenotype in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick type C2 disease
Abstract
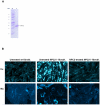
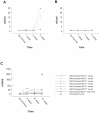
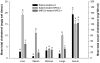
Niemann-Pick type C2 (NPC2) disease is a fatal autosomal recessive neurovisceral degenerative disorder characterized by late endosomal-lysosomal sequestration of low-density lipoprotein derived cholesterol. The breach in intracellular cholesterol homeostasis is caused by deficiency of functional NPC2, a soluble sterol binding protein targeted to the lysosomes by binding the mannose-6-phosphate receptor. As currently there is no effective treatment for the disorder, we have investigated the efficacy of NPC2 replacement therapy in a murine gene-trap model of NPC2-disease generated on the 129P2/OlaHsd genetic background. NPC2 was purified from bovine milk and its functional competence assured in NPC2-deficient fibroblasts using the specific cholesterol fluorescent probe filipin. For evaluation of phenotype correction in vivo, three-week-old NPC2(-/-) mice received two weekly intravenous injections of 5 mg/kg NPC2 until trial termination 66 days later. Whereas the saline treated NPC2(-/-) mice exhibited massive visceral cholesterol storage as compared to their wild-type littermates, administration of NPC2 caused a marked reduction in cholesterol build up. The histological findings, indicating an amelioration of the disease pathology in liver, spleen, and lungs, corroborated the biochemical results. Little or no difference in the overall cholesterol levels was observed in the kidneys, blood, cerebral cortex and hippocampus when comparing NPC2(-/-) and wild type mice. However, cerebellum cholesterol was increased about two fold in NPC2(-/-) mice compared with wild-type littermates. Weight gain performance was slightly improved as a result of the NPC2 treatment but significant motor coordination deficits were still observed. Accordingly, ultrastructural cerebellar abnormalities were detected in both saline treated and NPC2 treated NPC2(-/-) animals 87 days post partum. Our data indicate that protein replacement may be a beneficial therapeutic approach in the treatment of the visceral manifestations in NPC2 disease and further suggest that neurodegeneration is not secondary to visceral dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
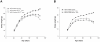
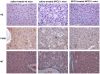

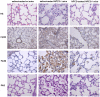

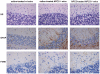
References
-
- Peake KB, Vance JE. Defective cholesterol trafficking in Niemann-Pick C-deficient cells. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:2731–2739. - PubMed
-
- Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, et al. Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1997;277:228–231. - PubMed
-
- Naureckiene S, Sleat DE, Lackland H, Fensom A, Vanier MT, et al. Identification of HE1 as the second gene of Niemann-Pick C disease. Science. 2000;290:2298–2301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

