Validation of three-dimensional echocardiography for quantification of aortic root geometry: comparison with multi-detector computed tomography
- PMID: 22073322
- PMCID: PMC3209591
- DOI: 10.4250/jcu.2011.19.3.128
Validation of three-dimensional echocardiography for quantification of aortic root geometry: comparison with multi-detector computed tomography
Abstract
Background: Three-dimensional (3D) echocardiography has been reported to be valuable for evaluating the geometry of cardiac chambers. We validated the accuracy of 3D transthoracic echocardiography for quantifying aortic root geometry in comparison with cardiac multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT).
Methods: Twenty-three patients who underwent cardiac MDCT and showed normal left ventricular ejection fraction (> 55%), as assessed by 2-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography, were enrolled (12 male, mean 53 ± 9 years). We defined the aortic root volume as the volume from the aortic annulus to the sinotubular junction. The aortic root volume at end-diastole measured by both cardiac MDCT and 3D echocardiography was assessed.
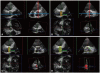
Results: The cross-sectional area of the aortic root was asymmetric. At the annulus level, the cross-sectional area showed asymmetric triangle. From the aortic annulus to the most dilated point of the sinus of Valsalva, the asymmetric triangular shape was maintained. From the most dilated point of the sinus of Valsalva to the sinotubular junction, the cross-sectional shape of the aortic root changed to oval. The average aortic root volumes measured by 3D echocardiography (ARV-3DE) were 13.6 ± 4.8 mL at end-diastole and 14.1 ± 5.3 mL at end-systole, respectively. The average aortic root volume measured by MDCT at end-diastole (ARV-CT) was 14.1 ± 5.7 mL. At end-diastole, the ARV-3DE correlated well with the ARV-CT (R(2) = 0.926, difference = 0.5 ± 1.7 mL), and the two methods were in excellent agreement (the percent difference was 0%).
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate both the feasibility and accuracy of 3D echocardiography for the clinical assessment of the geometry of the aortic root.
Keywords: Aortic root geometry; Cardiac multi-detector computed tomography; Three-dimensional echocardiography.
Figures




References
-
- Nkomo VT, Gardin JM, Skelton TN, Gottdiener JS, Scott CG, Enriquez-Sarano M. Burden of valvular heart diseases: a population-based study. Lancet. 2006;368:1005–1011. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RH, Lal M, Ho SY. Anatomy of the aortic root with particular emphasis on options for its surgical enlargement. J Heart Valve Dis. 1996;5(Suppl 3):S249–S257. - PubMed
-
- Lansac E, Lim HS, Shomura Y, Lim KH, Rice NT, Goetz W, Acar C, Duran CM. A four-dimensional study of the aortic root dynamics. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2002;22:497–503. - PubMed
-
- Tops LF, Wood DA, Delgado V, Schuijf JD, Mayo JR, Pasupati S, Lamers FP, van der Wall EE, Schalij MJ, Webb JG, Bax JJ. Noninvasive evaluation of the aortic root with multislice computed tomography implications for transcatheter aortic valve replacement. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2008;1:321–330. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

