Gallium compound GaQ(3) -induced Ca(2+) signalling triggers p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cancer cells
- PMID: 22074401
- PMCID: PMC3417493
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01780.x
Gallium compound GaQ(3) -induced Ca(2+) signalling triggers p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis in cancer cells
Erratum in
- Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Feb;173(3):627
-
Erratum.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 Feb;173(3):627. doi: 10.1111/bph.13412. Epub 2016 Jan 27. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 31265508 Free PMC article.
Abstract
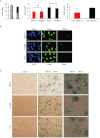
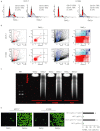
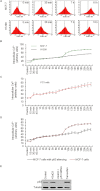
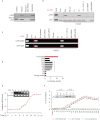
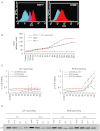
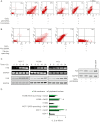
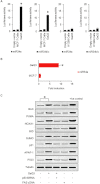
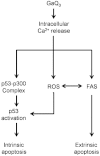
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE A novel anti-neoplastic gallium complex GaQ(3) (KP46), earlier developed by us, is currently in phase I clinical trial. GaQ(3) induced S-phase arrest and apoptosis via caspase/PARP cleavage in a variety of cancers. However, the underlying mechanism of apoptosis is unknown. Here, we have explored the mechanism(s) of GaQ(3) -induced apoptosis in cancer cells, focusing on p53 and intracellular Ca(2+) signalling. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH GaQ(3) -induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis were determined in cancer cell lines, with different p53 status (p53(+/+) , p53(-/-) and p53 mutant). Time course analysis of intracellular Ca(2+) calcium release, p53 promoter activation, p53-nuclear/cytoplasmic movements and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were conducted. Ca(2+) -dependent formation of the p53-p300 transcriptional complex was analysed by co-immunoprecipitation and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Ca(2+) signalling, p53, p300 and ROS were serially knocked down to study Ca(2+) -p53-ROS ineractions in GaQ(3) -induced apoptosis. KEY RESULTS GaQ(3) triggered intracellular Ca(2+) release stabilizing p53-p300 complex and recruited p53 to p53 promoter, leading to p53 mRNA and protein synthesis. p53 induced higher intracellular Ca(2+) release and ROS followed by activation of p53 downstream genes including those for the micro RNA mir34a. In p53(-/-) and p53 mutant cells, GaQ(3) -induced Ca(2+) -signalling generated ROS. ROS further increased membrane translocation of FAS and FAS-mediated extrinsic apoptosis. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS This study disclosed a novel mechanism of Ca(2+) -signalling-mediated p53 activation and ROS up-regulation. Understanding the mechanism of GaQ(3) -induced apoptosis will help establish this gallium-based organic compound as a potent anti-cancer drug.
© 2011 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology © 2011 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Barton C, Davies D, Balkwill F, Burke F. Involvement of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in IFN-gamma-induced apoptosis that are enhanced with cisplatin. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:1474–1486. - PubMed
-
- Bennett M, Macdonald K, Chan SW, Luzio JP, Simari R, Weissberg P. Cell surface trafficking of Fas: a rapid mechanism of p53-mediated apoptosis. Science. 1998;282:290–293. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Camello-Almaraz C, Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Pozo MJ, Camello PJ. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and Ca2+ signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2006;291:C1082–C1088. - PubMed
-
- Campaner S, Spreafico F, Burgold T, Doni M, Rosato U, Amati B, et al. The Methyltransferase Set7/9 (Setd7) Is Dispensable for the p53-Mediated DNA Damage Response In Vivo. Mol Cell. 2011;43:681–688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

