Femtosecond infrared intrastromal ablation and backscattering-mode adaptive-optics multiphoton microscopy in chicken corneas
- PMID: 22076258
- PMCID: PMC3207366
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.2.002950
Femtosecond infrared intrastromal ablation and backscattering-mode adaptive-optics multiphoton microscopy in chicken corneas
Abstract
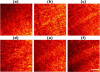
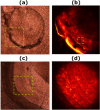
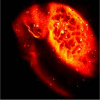
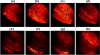
The performance of femtosecond (fs) laser intrastromal ablation was evaluated with backscattering-mode adaptive-optics multiphoton microscopy in ex vivo chicken corneas. The pulse energy of the fs source used for ablation was set to generate two different ablation patterns within the corneal stroma at a certain depth. Intrastromal patterns were imaged with a custom adaptive-optics multiphoton microscope to determine the accuracy of the procedure and verify the outcomes. This study demonstrates the potential of using fs pulses as surgical and monitoring techniques to systematically investigate intratissue ablation. Further refinement of the experimental system by combining both functions into a single fs laser system would be the basis to establish new techniques capable of monitoring corneal surgery without labeling in real-time. Since the backscattering configuration has also been optimized, future in vivo implementations would also be of interest in clinical environments involving corneal ablation procedures.
Keywords: (170.1020) Ablation of tissue; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.4470) Ophthalmology; (180.4315) Nonlinear microscopy.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Second-harmonic generation microscopy of photocurable polymer intrastromal implants in ex-vivo corneas.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 May 22;6(6):2211-9. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.002211. eCollection 2015 Jun 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26114039 Free PMC article.
-
Corneal multiphoton microscopy and intratissue optical nanosurgery by nanojoule femtosecond near-infrared pulsed lasers.Ann Anat. 2006 Sep;188(5):395-409. doi: 10.1016/j.aanat.2006.02.006. Ann Anat. 2006. PMID: 16999201
-
Multiphoton microscopy for monitoring intratissue femtosecond laser surgery effects.Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jul;39(6):527-33. doi: 10.1002/lsm.20523. Lasers Surg Med. 2007. PMID: 17659583
-
Histological analysis of a cornea following experimental femtosecond laser ablation.Cornea. 2014 Nov;33 Suppl 11:S19-24. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000251. Cornea. 2014. PMID: 25289720 Review.
-
Ultrafast (femtosecond) laser refractive surgery.Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002 Aug;13(4):246-9. doi: 10.1097/00055735-200208000-00011. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002. PMID: 12165709 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of the corneal collagen organization after chemical burn using second harmonic generation microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Jan 11;12(2):756-765. doi: 10.1364/BOE.412819. eCollection 2021 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 33680540 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of spatial lamellar distribution from adaptive-optics second harmonic generation corneal images.Biomed Opt Express. 2013 Jun 4;4(7):1006-13. doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.001006. Print 2013 Jul 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2013. PMID: 23847727 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in optics for biotechnology, medicine and surgery.Biomed Opt Express. 2012 Mar 1;3(3):531-2. doi: 10.1364/BOE.3.000531. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Biomed Opt Express. 2012. PMID: 22435099 Free PMC article.
-
Photo-induced processes in collagen-hypericin system revealed by fluorescence spectroscopy and multiphoton microscopy.Biomed Opt Express. 2014 Apr 2;5(5):1355-62. doi: 10.1364/BOE.5.001355. eCollection 2014 May 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2014. PMID: 24877000 Free PMC article.
-
Second-harmonic generation microscopy of photocurable polymer intrastromal implants in ex-vivo corneas.Biomed Opt Express. 2015 May 22;6(6):2211-9. doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.002211. eCollection 2015 Jun 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2015. PMID: 26114039 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krasnov M. M., “Q-switched laser goniopuncture,” Arch. Ophthalmol. 92(1), 37–41 (1974). - PubMed
-
- Aron-Rosa D., Aron J. J., Griesemann M., Thyzel R., “Use of the neodymium-YAG laser to open the posterior capsule after lens implant surgery: a preliminary report,” J. Am. Intraocul. Implant Soc. 6(4), 352–354 (1980). - PubMed
-
- Klapper R. M., “Q-switched neodymium:YAG laser iridotomy,” Ophthalmology 91(9), 1017–1021 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Vogel A., Noack A., Nahen K., Theisen D., Birngruber R., Hammer D. X., Noojin G. D., Rockwell B. A., “Laser-induced breakdown in the eye at pulse durations from 80 ns to 100 fs,” Proc. SPIE 3255, 43–49 (1998).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
