Double-clad fiber with a tapered end for confocal endomicroscopy
- PMID: 22076259
- PMCID: PMC3207367
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.2.002961
Double-clad fiber with a tapered end for confocal endomicroscopy
Abstract
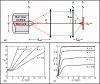
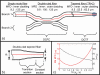
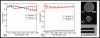
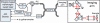
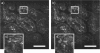
We present a double-clad fiber coupler (DCFC) for use in confocal endomicroscopy to reduce speckle contrast, increase signal collection while preserving optical sectioning. The DCFC is made by incorporating a double-clad tapered fiber (DCTF) to a fused-tapered DCFC for achromatic transmission (from 1265 nm to 1325 nm) of > 95% illumination light trough the single mode (SM) core and collection of > 40% diffuse light through inner cladding modes. Its potential for confocal endomicroscopy is demonstrated in a spectrally-encoded imaging setup which shows a 3 times reduction in speckle contrast as well as 5.5 × increase in signal collection compared to imaging with a SM fiber.
Keywords: (030.6140) Speckle; (060.2340) Fiber optics components; (110.2990) Image formation theory; (170.1790) Confocal microscopy; (170.2150) Endoscopic imaging.
Figures
References
-
- Kiesslich R., Burg J., Vieth M., Gnaendiger J., Enders M., Delaney P., Polglase A., McLaren W., Janell D., Thomas S., Nafe B., Galle P. R., Neurath M. F., “Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo,” Gastroenterology 127, 706–713 (2004). 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.06.050 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Buchner A. M., Shahid M. W., Heckman M. G., Krishna M., Ghabril M., Hasan M., Crook J. E., Gomez V., Raimondo M., Woodward T., Wolfsen H. C., Wallace M. B., “Comparison of probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy with virtual chromoendoscopy for classification of colon polyps,” Gastroenterology 138, 834–842 (2010). 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.10.053 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Carlson K., Pavlova I., Collier T., Descour M., Follen M., Richards-Kortum R., “Confocal microscopy: Imaging cervical precancerous lesions,” Gynecologic Oncology 99, S84–S88 (2005), The 4th International Conference on Cervical Cancer with a Day of Spiritual, Psychological, Complementary, and Alternative Treatment of Cancer and Pain. 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.07.049 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
