tRNAs marked with CCACCA are targeted for degradation
- PMID: 22076379
- PMCID: PMC3273417
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1213671
tRNAs marked with CCACCA are targeted for degradation
Abstract
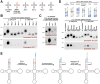
The CCA-adding enzyme [ATP(CTP):tRNA nucleotidyltransferase] adds CCA to the 3' ends of transfer RNAs (tRNAs), a critical step in tRNA biogenesis that generates the amino acid attachment site. We found that the CCA-adding enzyme plays a key role in tRNA quality control by selectively marking structurally unstable tRNAs and tRNA-like small RNAs for degradation. Instead of adding CCA to the 3' ends of these transcripts, CCA-adding enzymes from all three kingdoms of life add CCACCA. In addition, hypomodified mature tRNAs are subjected to CCACCA addition as part of a rapid tRNA decay pathway in vivo. We conjecture that CCACCA addition is a universal mechanism for controlling tRNA levels and preventing errors in translation.
Figures
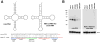


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

