Change in self-efficacy, autonomous and controlled motivation predicting smoking
- PMID: 22076554
- PMCID: PMC3549683
- DOI: 10.1177/1359105311422457
Change in self-efficacy, autonomous and controlled motivation predicting smoking
Abstract
Although motivational interviewing (MI) has been shown to be effective in changing health behaviors, its effects on smoking cessation have been mixed. The purpose of the present study is to assess factors of motivation and self-efficacy as they mediate the relationship between MI and smoking cessation. This is a secondary analysis of an MI based smoking cessation randomized trial. MI counseling was associated with change in smoking behaviors during a 12 months intervention but was not related to autonomous motivation, controlled motivation, or self-efficacy at baseline and 6 months, the hypothesized mediators. This study confirmed the pathway to quit smoking through increase in self-efficacy.
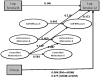
Figures
References
-
- Amrhein PC, Miller WR, Yahne CE, Palmer M, Fulcher L. Client commitment language during motivational interviewing predicts drug use outcomes. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2003;71(5):862–878. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Self efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: Freeman; 1997.
-
- Baranowski T, Cullen KW, Baranowski J. Psychosocial correlates of dietary intake: advancing dietary intervention. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:17–40. - PubMed
-
- Baron RM, Kenny DA. The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1986;51(6):1173–1182. - PubMed
-
- Berg CJ, Cox LS, Nazir N, Mussulman L, Ahluwalia JS, Ellerbeck EF. Correlates of home smoking restrictions among rural smokers. Nicotine and Tobacco Research. 2006;8(3):353–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

