Biphasic peptide amphiphile nanomatrix embedded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for stimulated osteoinductive response
- PMID: 22077993
- PMCID: PMC3691849
- DOI: 10.1021/nn203247m
Biphasic peptide amphiphile nanomatrix embedded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for stimulated osteoinductive response
Abstract
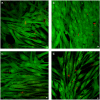
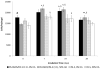
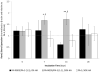
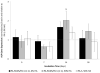
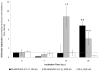
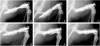
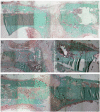
Formation of the native bone extracellular matrix (ECM) provides an attractive template for bone tissue engineering. The structural support and biological complexity of bone ECM are provided within a composite microenvironment that consists of an organic fibrous network reinforced by inorganic hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles. Recreating this biphasic assembly, a bone ECM analogous scaffold comprising self-assembling peptide amphiphile (PA) nanofibers and interspersed HA nanoparticles was investigated. PAs were endowed with biomolecular ligand signaling using a synthetically inscribed peptide sequence (i.e., RGDS) and integrated with HA nanoparticles to form a biphasic nanomatrix hydrogel. It was hypothesized the biphasic hydrogel would induce osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) and improve bone healing as mediated by RGDS ligand signaling within PA nanofibers and embedded HA mineralization source. Viscoelastic stability of the biphasic PA hydrogels was evaluated with different weight concentrations of HA for improved gelation. After demonstrating initial viability, long-term cellularity and osteoinduction of encapsulated hMSCs in different PA hydrogels were studied in vitro. Temporal progression of osteogenic maturation was assessed by gene expression of key markers. A preliminary animal study demonstrated bone healing capacity of the biphasic PA nanomatrix under physiological conditions using a critical size femoral defect rat model. The combination of RGDS ligand signaling and HA nanoparticles within the biphasic PA nanomatrix hydrogel demonstrated the most effective osteoinduction and comparative bone healing response. Therefore, the biphasic PA nanomatrix establishes a well-organized scaffold with increased similarity to natural bone ECM with the prospect for improved bone tissue regeneration.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle reinforced peptide amphiphile nanomatrix enhances the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by compositional ratios.Acta Biomater. 2012 Nov;8(11):4053-63. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2012.07.024. Epub 2012 Jul 25. Acta Biomater. 2012. PMID: 22842043 Free PMC article.
-
RGD-bearing peptide-amphiphile-hydroxyapatite nanocomposite bone scaffold: an in vitro study.Biomed Mater. 2013 Aug;8(4):045014. doi: 10.1088/1748-6041/8/4/045014. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Biomed Mater. 2013. PMID: 23860136
-
Osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells directed by extracellular matrix-mimicking ligands in a biomimetic self-assembled peptide amphiphile nanomatrix.Biomacromolecules. 2009 Oct 12;10(10):2935-44. doi: 10.1021/bm9007452. Biomacromolecules. 2009. PMID: 19746964 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic hydroxyapatite-containing composite nanofibrous substrates for bone tissue engineering.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2010 Apr 28;368(1917):2065-81. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2010.0012. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2010. PMID: 20308115 Review.
-
Multifunctional materials for bone cancer treatment.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014 May 28;9:2713-25. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S55943. eCollection 2014. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24920907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Progress and challenges of the bioartificial pancreas.Nano Converg. 2016;3(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s40580-016-0088-4. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Nano Converg. 2016. PMID: 28191438 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of HIF-1α in Bone Regeneration: A New Direction and Challenge in Bone Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 28;24(9):8029. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098029. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced Therapeutic and Long-Term Dynamic Vascularization Effects of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Endothelial Cells Encapsulated in a Nanomatrix Gel.Circulation. 2017 Nov 14;136(20):1939-1954. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026329. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28972000 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole encapsulated biomimetic nanomatrix gel on Enterococcus faecalis and Treponema denticola.Biomater Res. 2015 Jun;19:9. doi: 10.1186/s40824-015-0032-4. Biomater Res. 2015. PMID: 26257918 Free PMC article.
-
Osteogenesis effects of magnetic nanoparticles modified-porous scaffolds for the reconstruction of bone defect after bone tumor resection.Regen Biomater. 2019 Dec;6(6):373-381. doi: 10.1093/rb/rbz019. Epub 2019 May 29. Regen Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31827889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rosso F, Giordano A, Barbarisi M, Barbarisi A. From Cell-ECM Interactions to Tissue Engineering. J. Cell. Physiol. 2004;199:174–180. - PubMed
-
- Streuli C. Extracellular Matrix Remodelling and Cellular Differentiation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999;11:634–640. - PubMed
-
- Rho J-Y, Kuhn-Spearing L, Zioupos P. Mechanical Properties and the Hierarchical Structure of Bone. Med. Eng. Phys. 1998;20:92–102. - PubMed
-
- Supova M. Problem of Hydroxyapatite Dispersion in Polymer Matrices: A Review. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 2009;20:1201–1213. - PubMed
-
- Benoit DS, Durney AR, Anseth KS. The Effect of Heparin-Functionalized PEG Hydrogels on Three-Dimensional Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Osteogenic Differentiation. Biomaterials. 2007;28:66–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

