Neuroplasticity subserving motor skill learning
- PMID: 22078504
- PMCID: PMC3217208
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.10.008
Neuroplasticity subserving motor skill learning
Abstract
Recent years have seen significant progress in our understanding of the neural substrates of motor skill learning. Advances in neuroimaging provide new insight into functional reorganization associated with the acquisition, consolidation, and retention of motor skills. Plastic changes involving structural reorganization in gray and white matter architecture that occur over shorter time periods than previously thought have been documented as well. Data from experimental animals provided crucial information on plausible cellular and molecular substrates contributing to brain reorganization underlying skill acquisition in humans. Here, we review findings demonstrating functional and structural plasticity across different spatial and temporal scales that mediate motor skill learning while identifying converging areas of interest and possible avenues for future research.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
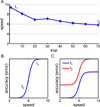


References
-
- Adcock RA, Thangavel A, Whitfield-Gabrieli S, Knutson B, Gabrieli JD. Reward-motivated learning: mesolimbic activation precedes memory formation. Neuron. 2006;50:507–517. - PubMed
-
- Albouy G, Sterpenich V, Balteau E, Vandewalle G, Desseilles M, Dang-Vu T, Darsaud A, Ruby P, Luppi PH, Degueldre C, et al. Both the hippocampus and striatum are involved in consolidation of motor sequence memory. Neuron. 2008;58:261–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

