Toward the fourth dimension of membrane protein structure: insight into dynamics from spin-labeling EPR spectroscopy
- PMID: 22078555
- PMCID: PMC3224804
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2011.10.009
Toward the fourth dimension of membrane protein structure: insight into dynamics from spin-labeling EPR spectroscopy
Abstract
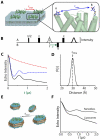
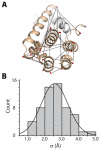
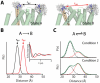
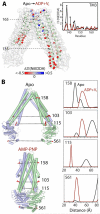
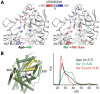
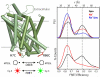
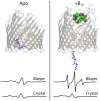
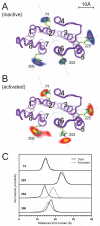
Trapping membrane proteins in the confines of a crystal lattice obscures dynamic modes essential for interconversion between multiple conformations in the functional cycle. Moreover, lattice forces could conspire with detergent solubilization to stabilize a minor conformer in an ensemble thus confounding mechanistic interpretation. Spin labeling in conjunction with electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy offers an exquisite window into membrane protein dynamics in the native-like environment of a lipid bilayer. Systematic application of spin labeling and EPR identifies sequence-specific secondary structures, defines their topology and their packing in the tertiary fold. Long range distance measurements (60 Å-80 Å) between pairs of spin labels enable quantitative analysis of equilibrium dynamics and triggered conformational changes. This review highlights the contribution of spin labeling to bridging structure and mechanism. Efforts to develop methods for determining structures from EPR restraints and to increase sensitivity and throughput promise to expand spin labeling applications in membrane protein structural biology.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
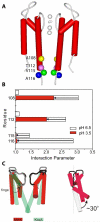
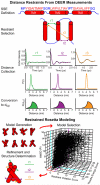
References
-
- Abramson J, Smirnova I, Kasho V, Verner G, Kaback HR, Iwata S. Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science. 2003;301:610–615. - PubMed
-
- Altenbach C, Marti T, Khorana HG, Hubbell WL. Transmembrane protein structure: spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Science. 1990;248:1088–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

