Programmed cell death in animal development and disease
- PMID: 22078876
- PMCID: PMC4511103
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.033
Programmed cell death in animal development and disease
Erratum in
- Cell. 2011 Dec 23;147(7):1640
Abstract
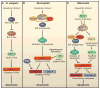
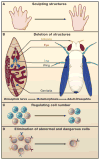
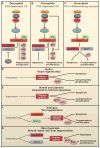
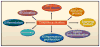
Programmed cell death (PCD) plays a fundamental role in animal development and tissue homeostasis. Abnormal regulation of this process is associated with a wide variety of human diseases, including immunological and developmental disorders, neurodegeneration, and cancer. Here, we provide a brief historical overview of the field and reflect on the regulation, roles, and modes of PCD during animal development. We also discuss the function and regulation of apoptotic proteins, including caspases, the key executioners of apoptosis, and review the nonlethal functions of these proteins in diverse developmental processes, such as cell differentiation and tissue remodeling. Finally, we explore a growing body of work about the connections between apoptosis, stem cells, and cancer, focusing on how apoptotic cells release a variety of signals to communicate with their cellular environment, including factors that promote cell division, tissue regeneration, and wound healing.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelwahid E, Pelliniemi LJ, Jokinen E. Cell death and differentiation in the development of the endocardial cushion of the embryonic heart. Microsc Res Tech. 2002;58:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Abdelwahid E, Yokokura T, Krieser RJ, Balasundaram S, Fowle WH, White K. Mitochondrial disruption in Drosophila apoptosis. Dev Cell. 2007;12:793–806. - PubMed
-
- Abraham MC, Lu Y, Shaham S. A morphologically conserved nonapoptotic program promotes linker cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Cell. 2007;12:73–86. - PubMed
-
- Abraham MC, Shaham S. Death without caspases, caspases without death. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:184–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

