Effects of A-CREB, a dominant negative inhibitor of CREB, on the expression of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the rat SON during hyperosmotic stimulation in vivo
- PMID: 22079318
- PMCID: PMC5079538
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.10.033
Effects of A-CREB, a dominant negative inhibitor of CREB, on the expression of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the rat SON during hyperosmotic stimulation in vivo
Abstract
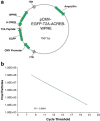
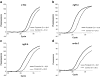
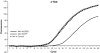
Intraperitoneal administration of hypertonic saline to the rat supraoptic nucleus (SON) increases the expression of several immediate early genes (IEG) and the vasopressin gene. These increases have usually been attributed to action of the cyclic-AMP Response Element Binding Protein (CREB). In this paper, we study the role of CREB in these events in vivo by delivering a potent dominant-negative form of CREB, known as A-CREB, to the rat SON through the use of an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector. Preliminary experiments on HEK 293 cells in vitro showed that the A-CREB vector that we used completely eliminated CREB-induced c-fos expression. We stereotaxically injected this AAV-A-CREB into one SON and a control AAV into the contralateral SON of the same rat. Two weeks following these injections we injected hypertonic saline intraperitoneally into the rat. Using this paradigm, we could measure the relative effects of inhibiting CREB on the induced expression of c-fos, ngfi-a, ngfi-b, and vasopressin genes in the A-CREB AAV injected SON versus the control AAV injected SON in the same rat. We found only a small (20%) decrease of c-fos expression and a 30% decrease of ngfi-b expression in the presence of the A-CREB. There were no significant changes in expression found in the other IEGs nor in vasopressin that were produced by the A-CREB. This suggests that CREB may play only a minor role in the expression of IEGs and vasopressin in the osmotically activated SON in vivo.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Boutillier AL, Barthel F, Roberts JL, Loeffler JP. Beta-adrenergic stimulation of cFOS via protein kinase A is mediated by cAMP regulatory element binding protein (CREB)-dependent and tissue-specific CREB-independent mechanisms in corticotrope cells. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:23520–23526. - PubMed
-
- Cahill MA, Janknecht R, Nordheim A. Signalling pathways: jack of all cascades. Curr Biol. 1996;6:16–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

