Restricted heterochromatin formation links NFATc2 repressor activity with growth promotion in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 22079596
- PMCID: PMC3626431
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.11.001
Restricted heterochromatin formation links NFATc2 repressor activity with growth promotion in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background & aims: Transcriptional silencing of the p15(INK4b) tumor suppressor pathway overcomes cellular protection against unrestrained proliferation in cancer. Here we show a novel pathway involving the oncogenic transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) c2 targeting a p15(INK4b)-mediated failsafe mechanism to promote pancreatic cancer tumor growth.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry, real-time polymerase chain reaction, immunoblotting, and immunofluorescence microscopy were used for expression studies. Cancer growth was assessed in vitro by [(3)H]thymidine incorporation, colony formation assays, and in vivo using xenograft tumor models. Protein-protein interactions, promoter regulation, and local histone modifications were analyzed by immunoprecipitation, DNA pull-down, reporter, and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays.
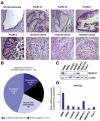
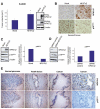
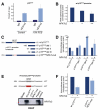
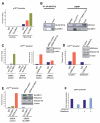
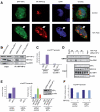
Results: Our study uncovered induction of NFATc2 in late-stage pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia lesions with increased expression in tumor cell nuclei of advanced cancers. In the nucleus, NFATc2 targets the p15(INK4b) promoter for inducible heterochromatin formation and silencing. NFATc2 binding to its cognate promoter site induces stepwise recruitment of the histone methyltransferase Suv39H1, causes local H3K9 trimethylation, and allows docking of heterochromatin protein HP1γ to the repressor complex. Conversely, inactivation of NFATc2 disrupts this repressor complex assembly and local heterochromatin formation, resulting in restoration of p15(INK4b) expression and inhibition of pancreatic cancer growth in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Here we describe a novel mechanism for NFATc2-mediated gene regulation and identify a functional link among its repressor activity, the silencing of the suppressor pathway p15(INK4b), and its pancreatic cancer growth regulatory functions. Thus, we provide evidence that inactivation of oncogenic NFATc2 might be an attractive strategy in treatment of pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2012 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

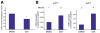
References
-
- Hidalgo M, Maitra A. The hedgehog pathway and pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:2094–2096. - PubMed
-
- Singh M, Maitra A. Precursor lesions of pancreatic cancer: molecular pathology and clinical implications. Pancreatology. 2007;7:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Kim WY, Sharpless NE. The regulation of INK4/ARF in cancer and aging. Cell. 2006;127:265–275. - PubMed
-
- Gil J, Peters G. Regulation of the INK4b-ARF-INK4a tumour suppressor locus: all for one or one for all. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:667–677. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

