A multicenter mortality prediction model for patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation
- PMID: 22080643
- PMCID: PMC3395423
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182387d43
A multicenter mortality prediction model for patients receiving prolonged mechanical ventilation
Abstract
Objective: Significant deficiencies exist in the communication of prognosis for patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation after acute illness, in part because of clinician uncertainty about long-term outcomes. We sought to refine a mortality prediction model for patients requiring prolonged ventilation using a multicentered study design.
Design: Cohort study.
Setting: Five geographically diverse tertiary care medical centers in the United States (California, Colorado, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Washington).
Patients: Two hundred sixty adult patients who received at least 21 days of mechanical ventilation after acute illness.
Interventions: None.
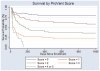
Measurements and main results: For the probability model, we included age, platelet count, and requirement for vasopressors and/or hemodialysis, each measured on day 21 of mechanical ventilation, in a logistic regression model with 1-yr mortality as the outcome variable. We subsequently modified a simplified prognostic scoring rule (ProVent score) by categorizing the risk variables (age 18-49, 50-64, and ≥65 yrs; platelet count 0-150 and >150; vasopressors; hemodialysis) in another logistic regression model and assigning points to variables according to β coefficient values. Overall mortality at 1 yr was 48%. The area under the curve of the receiver operator characteristic curve for the primary ProVent probability model was 0.79 (95% confidence interval 0.75-0.81), and the p value for the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit statistic was .89. The area under the curve for the categorical model was 0.77, and the p value for the goodness-of-fit statistic was .34. The area under the curve for the ProVent score was 0.76, and the p value for the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit statistic was .60. For the 50 patients with a ProVent score >2, only one patient was able to be discharged directly home, and 1-yr mortality was 86%.
Conclusion: The ProVent probability model is a simple and reproducible model that can accurately identify patients requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation who are at high risk of 1-yr mortality.
Figures
Comment in
-
Predictions of death compete with earthquake and tsunami predictions.Crit Care Med. 2012 Apr;40(4):1357-8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31823e94ea. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22425841 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cox CE, Carson SS, Holmes GM, et al. Increase in tracheostomy for prolonged mechanical ventilation in North Carolina, 1993–2002. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:2219–2226. - PubMed
-
- Zilberberg MD, de Wit M, Prirone JR, et al. Growth in adult prolonged acute mechanical ventilation: Implications for healthcare delivery. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1451–1455. - PubMed
-
- Carson SS, Bach PB. The epidemiology and costs of chronic critical illness. Crit Care Clin. 2002;18:461–476. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources