Abusive head trauma Part II: radiological aspects
- PMID: 22080958
- PMCID: PMC3306566
- DOI: 10.1007/s00431-011-1611-6
Abusive head trauma Part II: radiological aspects
Abstract
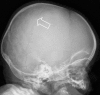
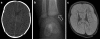
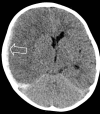
Abusive head trauma (AHT) is a relatively common cause of neurotrauma in young children. Radiology plays an important role in establishing a diagnosis and assessing a prognosis. Computed tomography (CT), followed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), is the best tool for neuroimaging. There is no evidence-based approach for the follow-up of AHT; both repeat CT and MRI are currently used but literature is not conclusive. A full skeletal survey according to international guidelines should always be performed to obtain information on possible underlying bone diseases or injuries suspicious for child abuse. Cranial ultrasonography is not indicated as a diagnostic modality for the evaluation of AHT. If there is a suspicion of AHT, this should be communicated with the clinicians immediately in order to arrange protective measures as long as AHT is part of the differential diagnosis.
Conclusion: The final diagnosis of AHT can never be based on radiological findings only; this should always be made in a multidisciplinary team assessment where all clinical and psychosocial information is combined and judged by a group of experts in the field.
Figures



References
-
- American College of Radiology (ACR) (2006). ACR practice guidelines for skeletal surveys in children. Last accessed 18-6-2011. http://www.acr.org/SecondaryMainMenuCategories/quality_safety/guidelines...
-
- Ashwal S, Babikian T, Gardner-Nichols J, Freier MC, Tong KA, Holshouser BA. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in assessment of outcome after pediatric traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006;87:S50–S58. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2006.07.275. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

