Mutant huntingtin, abnormal mitochondrial dynamics, defective axonal transport of mitochondria, and selective synaptic degeneration in Huntington's disease
- PMID: 22080977
- PMCID: PMC3249480
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.016
Mutant huntingtin, abnormal mitochondrial dynamics, defective axonal transport of mitochondria, and selective synaptic degeneration in Huntington's disease
Abstract
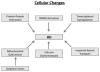
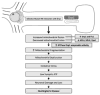
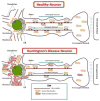
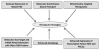
Huntington's disease (HD) is a progressive, fatal neurodegenerative disease caused by expanded polyglutamine repeats in the HD gene. HD is characterized by chorea, seizures, involuntary movements, dystonia, cognitive decline, intellectual impairment and emotional disturbances. Research into mutant huntingtin (Htt) and mitochondria has found that mutant Htt interacts with the mitochondrial protein dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1), enhances GTPase Drp1 enzymatic activity, and causes excessive mitochondrial fragmentation and abnormal distribution, leading to defective axonal transport of mitochondria and selective synaptic degeneration. This article summarizes latest developments in HD research and focuses on the role of abnormal mitochondrial dynamics and defective axonal transport in HD neurons. This article also discusses the therapeutic strategies that decrease mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal damage in HD.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Vonsattel JP, Myers RH, Stevens TJ, Ferrante RJ, Bird ED, Richardson EP. Neuropathological classification of Huntington’s disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1985;44:559–577. - PubMed
-
- Folstein SE. Huntington’s Disease. Johns Hopkins University Press; 1990.
-
- Ross CA, Tabrizi SJ. Huntington’s disease: from molecular pathogenesis to clinical treatment. Lancet Neurol. 2011;10:83–98. - PubMed
-
- Byers RK, Gilles FH, Fung C. Huntington’s disease in children: Neuropathologic study of four cases. Neurology. 1973;23:561–569. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

