Data mining approaches for genome-wide association of mood disorders
- PMID: 22081063
- PMCID: PMC3306768
- DOI: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e32834dc40d
Data mining approaches for genome-wide association of mood disorders
Abstract
Background: Mood disorders are highly heritable forms of major mental illness. A major breakthrough in elucidating the genetic architecture of mood disorders was anticipated with the advent of genome-wide association studies (GWAS). However, to date few susceptibility loci have been conclusively identified. The genetic etiology of mood disorders appears to be quite complex, and as a result, alternative approaches for analyzing GWAS data are needed. Recently, a polygenic scoring approach that captures the effects of alleles across multiple loci was successfully applied to the analysis of GWAS data in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder (BP). However, this method may be overly simplistic in its approach to the complexity of genetic effects. Data mining methods are available that may be applied to analyze the high dimensional data generated by GWAS of complex psychiatric disorders.
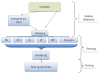
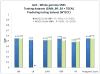
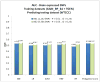
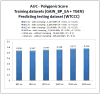
Results: We sought to compare the performance of five data mining methods, namely, Bayesian networks, support vector machine, random forest, radial basis function network, and logistic regression, against the polygenic scoring approach in the analysis of GWAS data on BP. The different classification methods were trained on GWAS datasets from the Bipolar Genome Study (2191 cases with BP and 1434 controls) and their ability to accurately classify case/control status was tested on a GWAS dataset from the Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium.
Conclusion: The performance of the classifiers in the test dataset was evaluated by comparing area under the receiver operating characteristic curves. Bayesian networks performed the best of all the data mining classifiers, but none of these did significantly better than the polygenic score approach. We further examined a subset of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes that are expressed in the brain, under the hypothesis that these might be most relevant to BP susceptibility, but all the classifiers performed worse with this reduced set of SNPs. The discriminative accuracy of all of these methods is unlikely to be of diagnostic or clinical utility at the present time. Further research is needed to develop strategies for selecting sets of SNPs likely to be relevant to disease susceptibility and to determine if other data mining classifiers that utilize other algorithms for inferring relationships among the sets of SNPs may perform better.
Figures
References
-
- Todd RD, Botteron KN. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. Vol. 11. WB Saunders; Philadelphia, PA: 2002. Etiology and genetics of early-onset Mood Disorders. Genetic contributions to early-onset psychopathology; pp. 449–518. - PubMed
-
- Merikangas KR, Low NC. The epidemiology of mood disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2004;6:411–421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U01 MH46282/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH079799/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA021237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059588/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH061675/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059556/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH60870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 MH093809/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059545/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- Z01 MH002810/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- 1Z01MH002810-01/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA21237/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059548/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH067257/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060870/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059534/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059571/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59535/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH59553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH46274/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH60068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059533/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH059565/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059586/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 MH59567/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH46280/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059553/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59566/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060879/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59587/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH060068/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States

