The prrAB two-component system is essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis viability and is induced under nitrogen-limiting conditions
- PMID: 22081401
- PMCID: PMC3256671
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.06258-11
The prrAB two-component system is essential for Mycobacterium tuberculosis viability and is induced under nitrogen-limiting conditions
Abstract
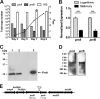
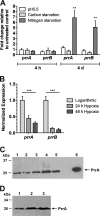
The Mycobacterium tuberculosis prrA-prrB (Rv0903c-Rv0902c) two-component regulatory system is expressed during intracellular growth in human macrophages and is required for early intracellular multiplication in murine macrophages, suggesting its importance in establishing infection. To better understand the function of the prrA-prrB two-component system, we defined the transcriptional characteristics of the prrA and prrB genes during exponential and stationary growth and upon exposure to different environmental stresses and attempted to generate a prrA-prrB deletion mutant. The prrA and prrB genes constitute an operon and are cotranscribed during logarithmic growth, with transcriptional levels decreasing in stationary phase and during hypoxia. Despite the transcriptional differences, PrrA protein levels remained relatively stable throughout growth and in hypoxia. Under conditions of nitrogen limitation, prrAB transcription was induced, while acidic pH stress and carbon starvation did not significantly alter transcript levels. Deletion of the prrAB operon on the chromosome of M. tuberculosis H37Rv occurred only in the presence of an episomal copy of the prrAB genes, indicating that this two-component system is essential for viability. Characterization of the prrAB locus in M. tuberculosis Mt21D3, a previously described prrA transposon mutant, revealed that this strain is not a true prrA knockout mutant. Rather, Tn5367 transposon insertion into the prrA promoter only decreased prrA and prrB transcription and PrrA levels in Mt21D3 compared to those in the parental Mt103 clinical strain. These data provide the first report describing the essentiality of the M. tuberculosis prrAB two-component system and reveal insights into its potential role in mycobacterial growth and metabolism.
Figures

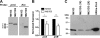
Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium smegmatis PrrAB two-component system influences triacylglycerol accumulation during ammonium stress.Microbiology (Reading). 2018 Oct;164(10):1276-1288. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000705. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Microbiology (Reading). 2018. PMID: 30084767
-
M. tuberculosis PrrA binds the dosR promoter and regulates mycobacterial adaptation to hypoxia.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024 Sep;148:102531. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2024.102531. Epub 2024 Jun 8. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2024. PMID: 38885567
-
Transient requirement of the PrrA-PrrB two-component system for early intracellular multiplication of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2002 May;70(5):2256-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.5.2256-2263.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11953357 Free PMC article.
-
Extra and intracellular expression of Mycobacterium tuberculosis genes.Tuber Lung Dis. 1998;79(2):91-7. doi: 10.1054/tuld.1998.0010. Tuber Lung Dis. 1998. PMID: 10645446 Review.
-
Adaptation to environmental stimuli within the host: two-component signal transduction systems of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Dec;75(4):566-82. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.05004-11. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22126994 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Transcription Machinery: Ready To Respond to Host Attacks.J Bacteriol. 2016 Apr 14;198(9):1360-73. doi: 10.1128/JB.00935-15. Print 2016 May. J Bacteriol. 2016. PMID: 26883824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis response to cholesterol is integrated with environmental pH and potassium levels via a lipid metabolism regulator.PLoS Genet. 2024 Jan 24;20(1):e1011143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011143. eCollection 2024 Jan. PLoS Genet. 2024. PMID: 38266039 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting multiple response regulators of Mycobacterium tuberculosis augments the host immune response to infection.Sci Rep. 2016 May 16;6:25851. doi: 10.1038/srep25851. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27181265 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting DosRST as a new approach to tuberculosis therapy.Future Med Chem. 2020 Mar;12(5):457-467. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2019-0263. Epub 2020 Feb 13. Future Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32053005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel RAYM_RS09735/RAYM_RS09740 Two-Component Signaling System Regulates Gene Expression and Virulence in Riemerella anatipestifer.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 21;8:688. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00688. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28484437 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardarov S, et al. 2002. Specialized transduction: an efficient method for generating marked and unmarked targeted gene disruptions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG and M. smegmatis. Microbiology 148: 3007–3017 - PubMed
-
- Betts JC, Lukey PT, Robb LC, McAdam RA, Duncan K. 2002. Evaluation of a nutrient starvation model of Mycobacterium tuberculosis persistence by gene and protein expression profiling. Mol. Microbiol. 43: 717–731 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

