Identification of novel GDNF isoforms and cis-antisense GDNFOS gene and their regulation in human middle temporal gyrus of Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 22081608
- PMCID: PMC3247946
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.310250
Identification of novel GDNF isoforms and cis-antisense GDNFOS gene and their regulation in human middle temporal gyrus of Alzheimer disease
Abstract
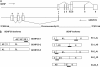
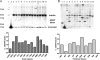
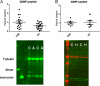
Primate-specific genes and isoforms could provide insight into human brain diseases. Our bioinformatic analysis revealed that there are possibly five isoforms of human GDNF gene with different pre- and pro-regions by inter- and intra-exon splicing. By using TaqMan primer probe sets, designed between exons, we verified the expression of all isoforms. Furthermore, a novel GDNFOS gene was found to be transcribed from the opposite strand of GDNF gene. GDNFOS gene has four exons that are spliced into different isoforms. GDNFOS1 and GDNFOS2 are long noncoding RNAs, and GDNFOS3 encodes a protein of 105 amino acids. To study human GDNF and GDNFOS regulation in neurodegenerative diseases, the protein and mRNA levels were measured by Western blot and RT-quantitative PCR, respectively, in postmortem middle temporal gyrus (MTG) of Alzheimer disease (AD) and Huntington disease (HD) patients in comparison with those of normal controls. In the MTG of AD patients, the mature GDNF peptide was down-regulated; however, the transcript of GDNF isoform from human exon 2 was up-regulated, whereas that of the conserved isoform from exon 1 remained unchanged in comparison with those of normal controls. In contrast, the mature GDNF peptide and the isoform mRNA levels were not changed in the MTG of HD. The findings of novel GDNF and GDNFOS isoforms and differences in tissue expression patterns dysregulated in AD brains may further reveal the role of endogenous GDNF in human brain diseases.
Figures


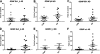
Similar articles
-
GDNFOS1 knockdown decreases the invasion and viability of glioblastoma cells.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Aug;18(2):1315-1322. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7670. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31316623 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel GDNF mRNA induced by LPS in immune cell lines.Neurosci Res. 2008 May;61(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2008.01.004. Epub 2008 Jan 17. Neurosci Res. 2008. PMID: 18295922
-
Time course of transient expression of pre-α-pro-GDNF and pre-β-pro-GDNF transcripts, and mGDNF mRNA region in Krushinsky-Molodkina rat brain after audiogenic seizures.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Jul;96:87-91. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 May 18. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31112899
-
The role of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor isoforms in human glial tumors.Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2022;86(6):106-112. doi: 10.17116/neiro202286061106. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko. 2022. PMID: 36534631 Review. English, Russian.
-
Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Bull. 2013 Aug;97:69-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2013.06.001. Epub 2013 Jun 10. Brain Res Bull. 2013. PMID: 23756188 Review.
Cited by
-
Failure of Glial Cell-Line Derived Neurotrophic Factor (GDNF) in Clinical Trials Orchestrated By Reduced NR4A2 (NURR1) Transcription Factor in Parkinson's Disease. A Systematic Review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Feb 24;13:645583. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.645583. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716718 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophins and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in the ovary: physiological and pathophysiological implications.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Mar 1;25(2):224-242. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmy047. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30608586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GDNFOS1 knockdown decreases the invasion and viability of glioblastoma cells.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Aug;18(2):1315-1322. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7670. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31316623 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA and its contribution to autism spectrum disorders.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017 Aug;23(8):645-656. doi: 10.1111/cns.12710. Epub 2017 Jun 20. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017. PMID: 28635106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the functional relevance of spatiotemporally-specific patterns of experience-dependent long noncoding RNA expression in the brain.RNA Biol. 2021 Jul;18(7):1025-1036. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1868165. Epub 2021 Jan 4. RNA Biol. 2021. PMID: 33397182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin L. F., Doherty D. H., Lile J. D., Bektesh S., Collins F. (1993) Science 260, 1130–1132 - PubMed
-
- Chiocco M. J., Harvey B. K., Wang Y., Hoffer B. J. (2007) Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 13, (Suppl. 3) S321–S328 - PubMed
-
- Airaksinen M. S., Saarma M. (2002) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 383–394 - PubMed
-
- Arenas E., Trupp M., Akerud P., Ibáñez C. F. (1995) Neuron 15, 1465–1473 - PubMed
-
- Henderson C. E., Phillips H. S., Pollock R. A., Davies A. M., Lemeulle C., Armanini M., Simmons L., Moffet B., Vandlen R. A., Simpson L. (1994) Science 266, 1062–1064 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

