Insights into the mechanism of onabotulinumtoxinA in chronic migraine
- PMID: 22082429
- PMCID: PMC3306767
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.02022.x
Insights into the mechanism of onabotulinumtoxinA in chronic migraine
Abstract
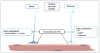
OnabotulinumtoxinA has recently been approved by regulatory agencies in the UK and United States for treatment of chronic migraine based on data generated from the PREEMPT studies. As such, onabotulinumtoxinA is the only prophylactic therapy specifically approved for chronic migraine. Most headache clinicians would agree that acute episodic migraine and chronic migraine differ in their pathophysiology, etiology, diagnosis, and response to pharmacological as well as nonpharmacological therapies. Of the 7 botulinum neurotoxin serotypes, botulinum neurotoxin type A (onabotulinumtoxinA) has been the most thoroughly investigated in preclinical and clinical studies. Based on preclinical studies, onabotulinumtoxinA is known to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters from both motor and sensory neurons by preventing vesicle fusion to the cell membrane. In addition to the well-documented myorelaxant effects of this neurotoxin, onabotulinumtoxinA can exert a direct analgesic effect that likely involves inhibition of primary and secondary nociceptive neurons. The inhibitory effects of onabotulinumtoxinA are also likely to involve suppressing the activity of myogenic trigger points and decreasing the persistent nociceptive barrage that promotes and maintains central sensitization. This article describes possible mechanisms to explain how onabotulinumtoxinA functions as a therapy for chronic migraine and considers why treatment with the neurotoxin is not effective in some chronic migraineurs.
© 2011 American Headache Society.
Figures
References
-
- Aurora SK, Dodick DW, Turkel CC, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 1 trial. Cephalalgia. 2010;30:793–803. - PubMed
-
- Diener HC, Dodick DW, Aurora SK, et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phase of the PREEMPT 2 trial. Cephalalgia. 2010;30:804–814. - PubMed
-
- Aurora SK, Gawel M, Brandes JL, Pokta S, Vandenburgh AM. Botulinum toxin type A prophylactic treatment of episodic migraine: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled exploratory study. Headache. 2007;47:486–499. - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld A. Botulinum toxin type A as an effective prophylactic treatment in primary headache disorders. Headache. 2003;43:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Relja M, Poole AC, Schoenen J, Pascual J, Lei X, Thompson C. A multicentre, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of multiple treatments of botulinum toxin type A (BoNTA) for the prophylaxis of episodic migraine headaches. Cephalalgia. 2007;27:492–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

