Basal breast cancer: a complex and deadly molecular subtype
- PMID: 22082486
- PMCID: PMC3343384
- DOI: 10.2174/156652412798376134
Basal breast cancer: a complex and deadly molecular subtype
Abstract
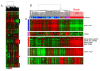
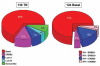
During the last decade, gene expression profiling of breast cancer has revealed the existence of five molecular subtypes and allowed the establishment of a new classification. The basal subtype, which represents 15-25% of cases, is characterized by an expression profile similar to that of myoepithelial normal mammary cells. Basal tumors are frequently assimilated to triple-negative (TN) breast cancers. They display epidemiological and clinico-pathological features distinct from other subtypes. Their pattern of relapse is characterized by frequent and early relapses and visceral locations. Despite a relative sensitivity to chemotherapy, the prognosis is poor. Recent characterization of their molecular features, such as the dysfunction of the BRCA1 pathway or the frequent expression of EGFR, provides opportunities for optimizing the systemic treatment. Several clinical trials dedicated to basal or TN tumors are testing cytotoxic agents and/or molecularly targeted therapies. This review summarizes the current state of knowledge of this aggressive and hard-to-treat subtype of breast cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Bertucci F, Houlgatte R, Nguyen C, et al. Gene expression profiling of cancer by use of DNA arrays: how far from the clinic? Lancet Oncol. 2001;2:674–82. - PubMed
-
- Sotiriou C, Piccart MJ. Taking gene-expression profiling to the clinic: when will molecular signatures become relevant to patient care? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:545–53. - PubMed
-
- Bertucci F, Finetti P, Cervera N, et al. Gene expression profiling and clinical outcome in breast cancer. Omics. 2006;10:429–43. - PubMed
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406:747–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
