Hyperpolarizing GABAergic transmission depends on KCC2 function and membrane potential
- PMID: 22082832
- PMCID: PMC3265795
- DOI: 10.4161/chan.5.6.17952
Hyperpolarizing GABAergic transmission depends on KCC2 function and membrane potential
Abstract
KCC2 comprises the major Cl(-) extruding mechanism in most adult neurons. Hyperpolarizing GABAergic transmission depends on KCC2 function. We recently demonstrated that glutamate reduces KCC2 function by a phosphorylation-dependent mechanism that leads to excitatory GABA responses. Here we investigated the methods by which to estimate changes in E(GABA), as well as the processes that lead to depolarizing GABA responses and their effects on neuronal excitability. We demonstrated that current-clamp recordings of membrane potential responses to GABA can determine upper and lower limits of E(GABA). We also further characterized depolarizing GABA responses, which both excited and inhibited neurons. Our analyses revealed that persistently active GABA(A) receptors contributed to loading Cl(-) during the glutamate exposure, indicating that tonic inhibition can facilitate the development of depolarizing GABA responses and increase excitability after pathophysiological insults. Finally, we demonstrated that hyperpolarizing GABA responses could temporarily switch to depolarizing responses when they coincided with an afterhyperpolarization.
Figures
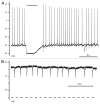
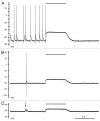
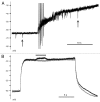
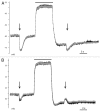
Comment on
-
NMDA receptor activity downregulates KCC2 resulting in depolarizing GABAA receptor-mediated currents.Nat Neurosci. 2011 Jun;14(6):736-43. doi: 10.1038/nn.2806. Epub 2011 May 1. Nat Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21532577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Payne JA, Stevenson TJ, Donaldson LF. Molecular characterization of a putative K-Cl cotransporter in rat brain. A neuronal-specific isoform. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16245–16252. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. Excitatory actions of GABA during development: the nature of the nurture. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2002;3:728–739. - PubMed
-
- Plotkin MD, Snyder EY, Hebert SC, Delpire E. Expression of the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter is developmentally regulated in postnatal rat brains: a possible mechanism underlying GABA's excitatory role in immature brain. J Neurobiol. 1997;33:781–795. - PubMed
-
- Blaesse P, Airaksinen MS, Rivera C, Kaila K. Cation-chloride cotransporters and neuronal function. Neuron. 2009;61:820–838. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
