Occludin: one protein, many forms
- PMID: 22083955
- PMCID: PMC3255790
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.06029-11
Occludin: one protein, many forms
Abstract
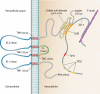
Intercellular tight junctions (TJs) exhibit a complex molecular architecture involving the regulated cointeraction of cytoplasmic adaptor proteins (e.g., zonula occludens) and integral membrane linker proteins (e.g., occludin and claudins). They provide structural integrity to epithelial and endothelial tissues and create highly polarized barriers essential to homeostatic maintenance within vertebrate physiological systems, while their dysregulation is an established pathophysiological hallmark of many diseases (e.g., cancer, stroke, and inflammatory lung disease). The junctional complex itself is a highly dynamic signaling entity wherein participant proteins constantly undergo a blend of regulatory modifications in response to diverse physiological and pathological cues, ultimately diversifying the overall adhesive properties of the TJ. Occludin, a 65-kDa tetraspan integral membrane protein, contributes to TJ stabilization and optimal barrier function. This paper reviews our current knowledge of how tissue occludin is specifically modified at the posttranscriptional and posttranslational levels in diverse circumstances, with associated consequences for TJ dynamics and epithelial/endothelial homeostasis. Mechanistic concepts such as splice variance and alternate promoter usage, proteolysis, phosphorylation, dimerization, and ubiquitination are comprehensively examined, and possible avenues for future investigation highlighted.
Figures

References
-
- Aijaz S, Balda MS, Matter K. 2006. Tight junctions: molecular architecture and function. Int. Rev. Cytol. 248:261–298 - PubMed
-
- András IE, et al. 2007. The NMDA and AMPA/KA receptors are involved in glutamate-induced alterations of occludin expression and phosphorylation in brain endothelial cells. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 27:1431–1443 - PubMed
-
- Andreeva AY, Krause E, Müller EC, Blasig IE, Utepbergenov DI. 2001. Protein kinase C regulates the phosphorylation and cellular localization of occludin. J. Biol. Chem. 276:38480–38486 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
