Reduced resolution transit delay prescan for quantitative continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging
- PMID: 22084006
- PMCID: PMC3367437
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.23103
Reduced resolution transit delay prescan for quantitative continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging
Abstract
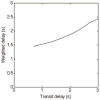
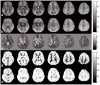
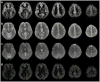
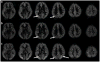
Arterial spin labeling perfusion MRI can suffer from artifacts and quantification errors when the time delay between labeling and arrival of labeled blood in the tissue is uncertain. This transit delay is particularly uncertain in broad clinical populations, where reduced or collateral flow may occur. Measurement of transit delay by acquisition of the arterial spin labeling signal at many different time delays typically extends the imaging time and degrades the sensitivity of the resulting perfusion images. Acquisition of transit delay maps at the same spatial resolution as perfusion images may not be necessary, however, because transit delay maps tend to contain little high spatial resolution information. Here, we propose the use of a reduced spatial resolution arterial spin labeling prescan for the rapid measurement of transit delay. Approaches to using the derived transit delay information to optimize and quantify higher resolution continuous arterial spin labeling perfusion images are described. Results in normal volunteers demonstrate heterogeneity of transit delay across different brain regions that lead to quantification errors without the transit maps and demonstrate the feasibility of this approach to perfusion and transit delay quantification.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Alsop DC, Detre JA, Grossman M. Assessment of cerebral blood flow in Alzheimer’s disease by spin-labeled magnetic resonance imaging. Annals of Neurology. 2000;47(1):93–100. - PubMed
-
- Detre JA, Alsop DC, Vives LR, Maccotta L, Teener JW, Raps EC. Noninvasive MRI evaluation of cerebral blood flow in cerebrovascular disease. Neurology. 1998;50(3):633–641. - PubMed
-
- Chalela JA, Alsop DC, Gonzalez-Atavales JB, Maldjian JA, Kasner SE, Detre JA. Magnetic resonance perfusion imaging in acute ischemic stroke using continuous arterial spin labeling. Stroke. 2000;31(3):680–687. - PubMed
-
- Calamante F, Gadian DG, Connelly A. Quantification of perfusion using bolus tracking magnetic resonance imaging in stroke: assumptions, limitations, and potential implications for clinical use. Stroke. 2002;33(4):1146–1151. - PubMed
-
- MacIntosh BJ, Lindsay AC, Kylintireas I, Kuker W, Gunther M, Robson MD, Kennedy J, Choudhury RP, Jezzard P. Multiple inflow pulsed arterial spin-labeling reveals delays in the arterial arrival time in minor stroke and transient ischemic attack. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31(10):1892–1894. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

