Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Continuous IV Infusion of LMWH: A Retrospective Study in 32 Children
- PMID: 22084672
- PMCID: PMC3195315
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/981497
Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis with Continuous IV Infusion of LMWH: A Retrospective Study in 32 Children
Abstract
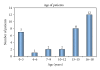
Thirty-two consecutive children aged 0-18 years with VTE treated with LMWH administered as a continuous infusion (CI) were identified at the Children's University Hospital Brno. The treatment led to at least partial resolution of the thrombus within two weeks in 85% of patients. There were no adverse events or increased bleeding reported in any patients. No recurrences were observed during a followup period of 6 months. Although continuous infusion should not replace subcutaneous (SC) administration of LMWH, CI appeared to be safe and efficient and may provide an alternate method of administering LMWH in a subset of the paediatric population where SC administration may not be feasible. Further prospective studies are needed to support the promising findings of our pilot clinical observation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis with continuous intravenous infusion of LMWH in children--an alternative to subcutaneous application when needed.Vnitr Lek. 2009 Mar;55(3):227-32. Vnitr Lek. 2009. PMID: 19378852
-
Efficacy of a low molecular weight heparin administered intravenously or subcutaneously in comparison with intravenous unfractionated heparin in the treatment of deep venous thrombosis. Certoparin-Study Group.Int Angiol. 1998 Sep;17(3):135-45. Int Angiol. 1998. PMID: 9821025 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis with fondaparinux or low molecular weight heparin in a large cohort of consecutive patients undergoing major orthopaedic surgery - findings from the ORTHO-TEP registry.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012 Dec;74(6):947-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04302.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22515679 Free PMC article.
-
Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) in the treatment of thrombosis.Eur J Med Res. 2004 Apr 30;9(4):225-39. Eur J Med Res. 2004. PMID: 15210403 Review.
-
Long-term use of different doses of low-molecular-weight heparin versus vitamin K antagonists in the treatment of venous thromboembolism.Ann Vasc Surg. 2010 Jul;24(5):628-39. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2009.08.006. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 19932949 Review.
Cited by
-
In situ crosslinkable heparin-containing poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels for sustained anticoagulant release.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012 Aug;100(8):2106-18. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34050. Epub 2012 May 21. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012. PMID: 22615105 Free PMC article.
-
Successful thrombolysis following enoxaparin therapy in two pediatric patients with congenital heart disease presenting with intracardiac and cerebral thrombosis.Thromb J. 2014 Sep 9;12:19. doi: 10.1186/1477-9560-12-19. eCollection 2014. Thromb J. 2014. PMID: 25278813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirsh J. Drug therapy: heparin. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1991;324(22):1565–1574. - PubMed
-
- Collins R, Scrimgeour A, Yusuf S, Peto R. Reduction in fatal pulmonary embolism and venous thrombosis by perioperative administration of subcutaneous heparin. Overview of results of randomized trials in general, orthopedic, and urologic surgery. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1988;318(18):1162–1173. - PubMed
-
- Castaman G, Rodeghiero F, Dini E. Thrombotic complications during L-asparaginase treatment for acute lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica. 1990;75(6):567–569. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein D, Coupey S, Schoenberg SK. Pulmonary embolism in adolescents. American Journal of Diseases of Children. 1986;140(7):667–671. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources