Subarachnoid-pleural fistula: applied anatomy of the thoracic spinal nerve root
- PMID: 22084743
- PMCID: PMC3196872
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/168959
Subarachnoid-pleural fistula: applied anatomy of the thoracic spinal nerve root
Abstract
Subarachnoid-pleural fistula (SPF) is a rare complication of chest or spine operations for neoplastic disease. Concomitant dural and parietal pleural defects permit flow of cerebrospinal fluid into the pleural cavity or intrapleural air into the subarachnoid space. Dural injury recognized intraoperatively permits immediate repair, but unnoticed damage may cause postoperative pleural effusion, intracranial hypotension, meningitis, or pneumocephalus. We review two cases of SPF following surgical intervention for chest wall metastatic disease to motivate a detailed review of the anatomy of neural, osseous, and ligamentous structures at the intervertebral foramen. We further provide recommendations for avoidance and detection of such complication.
Figures

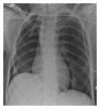
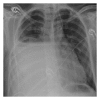
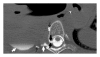
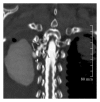

References
-
- Shimizu K, Otarii Y, Ibe T, Kawashima O, Kamiyoshihara M, Morishita Y. Successful treatment of subarachnoid-pleural fistula using pericardial fat pad and fibrin glue after chest wall resection for lung cancer. Japanese Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. 2005;53(2):93–96. - PubMed
-
- Kale BS, Kole SD. Duro-pleural fistula following ligation of patent ductus arteriosus. Indian Journal of Thoracic Cardiovascular Surgery. 2005;21:218–219.
-
- Monla-Hassan J, Eichenhorn M, Spickler E, Talati S, Nockels R, Hyzy R. Duropleural fistula manifested as a large pleural transudate: an unusual complication of transthoracic diskectomy. Chest. 1998;114(6):1786–1789. - PubMed
-
- Jahn K, Winkler K, Tiling R, Brandt T. Intracranial hypotension syndrome due to duropleural fistula after thoracic diskectomy. Journal of Neurology. 2001;248(12):1101–1103. - PubMed
-
- Hentschel SJ, Rhines LD, Wong FC, Gokaslan ZL, McCutcheon IE. Subarachnoid-pleural fistula after resection of thoracic tumors. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2004;100(supplement 4):332–336. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
