Secondary nucleating sequences affect kinetics and thermodynamics of tau aggregation
- PMID: 22085312
- PMCID: PMC3237831
- DOI: 10.1021/bi2014745
Secondary nucleating sequences affect kinetics and thermodynamics of tau aggregation
Abstract
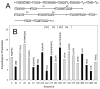
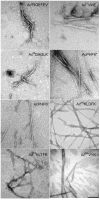
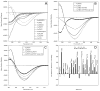
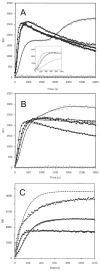
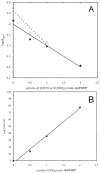
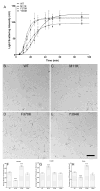
Tau protein was scanned for highly amyloidogenic sequences in amphiphilic motifs (X)(n)Z, Z(X)(n)Z (n ≥ 2), or (XZ)(n) (n ≥ 2), where X is a hydrophobic residue and Z is a charged or polar residue. N-Acetyl peptides homologous to these sequences were used to study aggregation. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) showed seven peptides, in addition to well-known primary nucleating sequences Ac(275)VQIINK (AcPHF6*) and Ac(306)VQIVYK (AcPHF6), formed fibers, tubes, ribbons, or rolled sheets. Of the peptides shown by TEM to form amyloid, Ac(10)VME, AcPHF6*, Ac(375)KLTFR, and Ac(393)VYK were found to enhance the fraction of β-structure of AcPHF6 formed at equilibrium, and Ac(375)KLTFR was found to inhibit AcPHF6 and AcPHF6* aggregation kinetics in a dose-dependent manner, consistent with its participation in a hybrid steric zipper model. Single site mutants were generated which transformed predicted amyloidogenic sequences in tau into non-amyloidogenic ones. A M11K mutant had fewer filaments and showed a decrease in aggregation kinetics and an increased lag time compared to wild-type tau, while a F378K mutant showed significantly more filaments. Our results infer that sequences throughout tau, in addition to PHF6 and PHF6*, can seed amyloid formation or affect aggregation kinetics or thermodynamics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prediction of nucleating sequences from amyloidogenic propensities of tau-related peptides.Biochemistry. 2006 Apr 11;45(14):4638-52. doi: 10.1021/bi052226q. Biochemistry. 2006. PMID: 16584199
-
Structure of core domain of fibril-forming PHF/Tau fragments.Biophys J. 2006 Mar 1;90(5):1774-89. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.070136. Epub 2005 Dec 9. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16339876 Free PMC article.
-
The formation of straight and twisted filaments from short tau peptides.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jun 25;279(26):26868-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402379200. Epub 2004 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15100221
-
Amyloidogenic peptide/single-walled carbon nanotube composites based on tau-protein-related peptides derived from AcPHF6: preparation and dispersive properties.J Phys Chem B. 2013 Jun 27;117(25):7593-604. doi: 10.1021/jp402057d. Epub 2013 Jun 19. J Phys Chem B. 2013. PMID: 23745842
-
Morphology of self-assembled structures formed by short peptides from the amyloidogenic protein tau depends on the solvent in which the peptides are dissolved.J Pept Sci. 2009 Oct;15(10):675-84. doi: 10.1002/psc.1172. J Pept Sci. 2009. PMID: 19714684
Cited by
-
Structure-based inhibitors of tau aggregation.Nat Chem. 2018 Feb;10(2):170-176. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2889. Epub 2017 Nov 20. Nat Chem. 2018. PMID: 29359764 Free PMC article.
-
Structural evaluations of tau protein conformation: methodologies and approaches.Biochem Cell Biol. 2017 Jun;95(3):338-349. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2016-0227. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Biochem Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28278386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blocking tau transmission by biomimetic graphene nanoparticles.J Mater Chem B. 2023 Aug 9;11(31):7378-7388. doi: 10.1039/d3tb00850a. J Mater Chem B. 2023. PMID: 37431684 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-Associated Mutations in Tau Encode for Changes in Aggregate Structure Conformation.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023 Dec 20;14(24):4282-4297. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00422. Epub 2023 Dec 6. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38054595 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping interactions with the chaperone network reveals factors that protect against tau aggregation.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018 May;25(5):384-393. doi: 10.1038/s41594-018-0057-1. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29728653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kosik KS, Greenberg SM. Tau proteins and Alzheimer disease. In: Terry RD, Katzman R, Bick KL, editors. Alzheimer Disease. Raven Press; New York: 1994. pp. 335–344.
-
- Mandelkow EM, Schweers O, Drewes G, Biernat J, Gustke N, Trinczek B, Mandelkow E. Structure, microtubule interactions, and phosphorylation of tau protein. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1996;777:96–106. - PubMed
-
- Friedhoff P, von Bergen M, Mandelkow E-M, Mandelkow E. Structure of tau protein and assembly into paired helical filaments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000;1502:122–132. - PubMed
-
- Mandelkow E-M, Mandelkow E. Tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Cell Biol. 1998;8:425–427. - PubMed
-
- Jeganathan S, Hascher A, Chinnathambi S, Biernat J, Mandelkow EM, Mandelkow E. Proline-directed pseudo-phosphorylation at AT8 and PHF1 epitopes induces a compaction of the paperclip folding of tau and generates a pathological (MC-1) conformation. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:32066–32076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

