Oxidation of HRas cysteine thiols by metabolic stress prevents palmitoylation in vivo and contributes to endothelial cell apoptosis
- PMID: 22085642
- PMCID: PMC3290434
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.11-189415
Oxidation of HRas cysteine thiols by metabolic stress prevents palmitoylation in vivo and contributes to endothelial cell apoptosis
Abstract
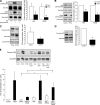
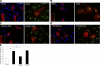
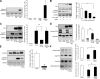
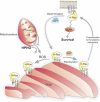
Here we demonstrate a new paradigm in redox signaling, whereby oxidants resulting from metabolic stress directly alter protein palmitoylation by oxidizing reactive cysteine thiolates. In mice fed a high-fat, high-sucrose diet and in cultured endothelial cells (ECs) treated with high palmitate and high glucose (HPHG), there was decreased HRas palmitoylation on Cys181/184 (61±24% decrease for cardiac tissue and 38±7.0% in ECs). This was due to oxidation of Cys181/184, detected using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight (MALDI TOF)-TOF. Decrease in HRas palmitoylation affected its compartmentalization and Ras binding domain binding activity, with a shift from plasma membrane tethering to Golgi localization. Loss of plasma membrane-bound HRas decreased growth factor-stimulated ERK phosphorylation (84±8.6% decrease) and increased apoptotic signaling (24±6.5-fold increase) after HPHG treatment that was prevented by overexpressing wild-type but not C181/184S HRas. The essential role of HRas in metabolic stress was made evident by the similar effects of expressing an inactive dominant negative N17-HRas or a MEK inhibitor. Furthermore, the relevance of thiol oxidation was demonstrated by overexpressing manganese superoxide dismutase, which improved HRas palmitoylation and ERK phosphorylation, while lessening apoptosis in HPHG treated ECs.
Figures


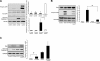
References
-
- Wright L. P., Philips M. R. (2006) Thematic review series: lipid posttranslational modifications. CAAX modification and membrane targeting of Ras. J. Lipid Res. 47, 883–891 - PubMed
-
- Rocks O., Peyker A., Kahms M., Verveer P. J., Koerner C., Lumbierres M., Kuhlmann J., Waldmann H., Wittinghofer A., Bastiaens P. I. (2005) An acylation cycle regulates localization and activity of palmitoylated Ras isoforms. Science 307, 1746–1752 - PubMed
-
- Hancock J. F., Paterson H., Marshall C. J. (1990) A polybasic domain or palmitoylation is required in addition to the CAAX motif to localize p21ras to the plasma membrane. Cell 63, 133–139 - PubMed
-
- Swarthout J. T., Lobo S., Farh L., Croke M. R., Greentree W. K., Deschenes R. J., Linder M. E. (2005) DHHC9 and GCP16 constitute a human protein fatty acyltransferase with specificity for H- and N-Ras. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 31141–31148 - PubMed
-
- Duncan J. A., Gilman A. G. (1998) A cytoplasmic acyl-protein thioesterase that removes palmitate from G protein alpha subunits and p21(RAS). J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15830–15837 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

