Mitogen-activated protein kinase in the amygdala plays a critical role in lithium chloride-induced taste aversion learning
- PMID: 22085719
- PMCID: PMC3532514
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2011.10.005
Mitogen-activated protein kinase in the amygdala plays a critical role in lithium chloride-induced taste aversion learning
Abstract
The intracellular mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in the brain is necessary for the formation of a variety of memories including conditioned taste aversion (CTA) learning. However, the functional role of MAPK activation in the amygdala during lithium chloride (LiCl)-induced CTA learning has not been established. In the present study, we investigated if local microinjection of SL327, a MAPK kinase inhibitor, into the rat amygdala could alleviate LiCl-induced CTA learning. Our results revealed that acute administration of a high dose of LiCl (0.15M, 12 ml/kg, i.p.) rapidly increased the level of phosphorylated MAPK (pMAPK)-positive cells in the central nucleus of the amygdala (CeA) and nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) of rats as measured by immunohistochemistry. Local microinjection of SL327 (1 μg/0.5 μl/hemisphere) into the CeA 10 min before LiCl administration decreased both the strength of LiCl-induced CTA paired with 0.125% saccharin and the level of LiCl-induced pMAPK-positive cells in the CeA, but not in the NTS. Our data suggest that the intracellular signaling cascade of the MAPK pathway in the CeA plays a critical role in the processing of visceral information induced by LiCl for CTA learning.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
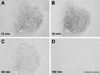
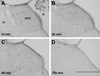





Similar articles
-
Area postrema lesions attenuate LiCl-induced c-Fos expression correlated with conditioned taste aversion learning.Physiol Behav. 2012 Jan 18;105(2):151-60. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.08.022. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Physiol Behav. 2012. PMID: 21889521 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of AP-1 family transcription factors in the amygdala during conditioned taste aversion learning: role for Fra-2.Brain Res. 2008 May 1;1207:128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.072. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18374904 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of efferents from the basolateral amygdala during the retrieval of conditioned taste aversion.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013 Nov;106:210-20. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 20. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2013. PMID: 24055778
-
N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester attenuates lithium-induced c-Fos, but not conditioned taste aversion, in rats.Neurosci Res. 2004 Dec;50(4):485-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2004.08.016. Neurosci Res. 2004. PMID: 15567487
-
Neural mechanisms of taste aversion learning.Neurosci Res. 1993 Mar;16(3):181-5. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(93)90122-7. Neurosci Res. 1993. PMID: 8387656 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of protein phosphorylation in the gustatory cortex and amygdala during taste learning.Exp Neurobiol. 2012 Jun;21(2):37-51. doi: 10.5607/en.2012.21.2.37. Epub 2012 Jun 12. Exp Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 22792024 Free PMC article.
-
Current Development Status of MEK Inhibitors.Molecules. 2017 Sep 26;22(10):1551. doi: 10.3390/molecules22101551. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28954413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acquisition and expression of conditioned taste aversion differentially affects extracellular signal regulated kinase and glutamate receptor phosphorylation in rat prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 May 7;8:153. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00153. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24847227 Free PMC article.
-
Parabrachial calcitonin gene-related peptide neurons mediate conditioned taste aversion.J Neurosci. 2015 Mar 18;35(11):4582-6. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3729-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25788675 Free PMC article.
-
Memory of conditioned taste aversion is erased by inhibition of PI3K in the insular cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013 Jun;38(7):1143-53. doi: 10.1038/npp.2013.20. Epub 2013 Jan 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23385661 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams JP, Sweatt JD. Molecular psychology: roles for the ERK MAP kinase cascade in memory. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2002;42:135–163. Review. - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD. The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nature Neuroscience. 1998;1:602–609. - PubMed
-
- Belelovsky K, Elkobi A, Kaphzan H, Nairn AC, Rosenblum K. A molecular switch for translational control in taste memory consolidation. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2005;22:2560–2568. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

