Increased in vivo inhibition of gene expression by combining RNA interference and U1 inhibition
- PMID: 22086952
- PMCID: PMC3245954
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr956
Increased in vivo inhibition of gene expression by combining RNA interference and U1 inhibition
Abstract
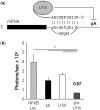
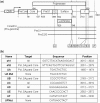
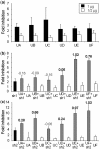
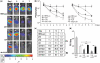
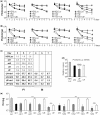
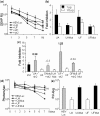
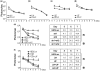
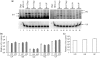
Inhibition of gene expression can be achieved with RNA interference (RNAi) or U1 small nuclear RNA-snRNA-interference (U1i). U1i is based on U1 inhibitors (U1in), U1 snRNA molecules modified to inhibit polyadenylation of a target pre-mRNA. In culture, we have shown that the combination of RNAi and U1i results in stronger inhibition of reporter or endogenous genes than that obtained using either of the techniques alone. We have now used these techniques to inhibit gene expression in mice. We show that U1ins can induce strong inhibition of the expression of target genes in vivo. Furthermore, combining U1i and RNAi results in synergistic inhibitions also in mice. This is shown for the inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) sequences or endogenous Notch1. Surprisingly, inhibition obtained by combining a U1in and a RNAi mediator is higher than that obtained by combining two U1ins or two RNAi mediators. Our results suggest that RNAi and U1i cooperate by unknown mechanisms to result in synergistic inhibitions. Analysis of toxicity and specificity indicates that expression of U1i inhibitors is safe. Therefore, we believe that the combination of RNAi and U1i will be a good option to block damaging endogenous genes, HBV and other infectious agents in vivo.
Figures
References
-
- Rivas FV, Tolia NH, Song JJ, Aragon JP, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Joshua-Tor L. Purified Argonaute2 and an siRNA form recombinant human RISC. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005;12:340–349. - PubMed
-
- Gunderson SI, Polycarpou-Schwarz M, Mattaj IW. U1 snRNP inhibits pre-mRNA polyadenylation through a direct interaction between U1 70K and poly(A) polymerase. Mol. Cell. 1998;1:255–264. - PubMed
-
- Fortes P, Cuevas Y, Guan F, Liu P, Pentlicky S, Jung SP, Martinez-Chantar ML, Prieto J, Rowe D, Gunderson SI. Inhibiting expression of specific genes in mammalian cells with 5' end-mutated U1 small nuclear RNAs targeted to terminal exons of pre-mRNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2003;100:8264–8269. - PMC - PubMed

