Direct, genome-wide assessment of DNA mutations in single cells
- PMID: 22086961
- PMCID: PMC3300019
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr949
Direct, genome-wide assessment of DNA mutations in single cells
Abstract
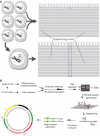
DNA mutations are the inevitable consequences of errors that arise during replication and repair of DNA damage. Because of their random and infrequent occurrence, quantification and characterization of DNA mutations in the genome of somatic cells has been difficult. Random, low-abundance mutations are currently inaccessible by standard high-throughput sequencing approaches because they cannot be distinguished from sequencing errors. One way to circumvent this problem and simultaneously account for the mutational heterogeneity within tissues is whole genome sequencing of a representative number of single cells. Here, we show elevated mutation levels in single cells from Drosophila melanogaster S2 and mouse embryonic fibroblast populations after treatment with the powerful mutagen N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. This method can be applied as a direct measure of exposure to mutagenic agents and for assessing genotypic heterogeneity within tissues or cell populations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid identification of a disease allele in mouse through whole genome sequencing and bulk segregation analysis.Genetics. 2011 Mar;187(3):633-41. doi: 10.1534/genetics.110.124586. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Genetics. 2011. PMID: 21196518 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide mutation detection by interclonal genetic variation.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2018 May-Jun;829-830:61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2018.03.011. Epub 2018 Apr 7. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2018. PMID: 29704995
-
Direct mutation analysis by high-throughput sequencing: from germline to low-abundant, somatic variants.Mutat Res. 2012 Jan 3;729(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2011.10.001. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Mutat Res. 2012. PMID: 22016070 Free PMC article. Review.
-
O-ethylthymidine adducts are the most relevant damages for mutation induced by N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea in female germ cells of Drosophila melanogaster.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2002;40(2):143-52. doi: 10.1002/em.10101. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2002. PMID: 12203408
-
A high-fidelity method for genomic sequencing of single somatic cells reveals a very high mutational burden.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jul;242(13):1318-1324. doi: 10.1177/1535370217717696. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28737476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms and consequences of aneuploidy and chromosome instability in the aging brain.Mech Ageing Dev. 2017 Jan;161(Pt A):19-36. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2016.03.007. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017. PMID: 27013377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic mutation load and spectra: A record of DNA damage and repair in healthy human cells.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2018 Oct;59(8):672-686. doi: 10.1002/em.22215. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2018. PMID: 30152078 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell, locus-specific bisulfite sequencing (SLBS) for direct detection of epimutations in DNA methylation patterns.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Aug 18;43(14):e93. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv366. Epub 2015 Apr 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25897117 Free PMC article.
-
Aging genomes: a necessary evil in the logic of life.Bioessays. 2014 Mar;36(3):282-92. doi: 10.1002/bies.201300127. Epub 2014 Jan 25. Bioessays. 2014. PMID: 24464418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of multiple displacement amplification (MDA) and multiple annealing and looping-based amplification cycles (MALBAC) in single-cell sequencing.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 8;9(12):e114520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114520. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25485707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Geigl JB, Speicher MR. Single-cell isolation from cell suspensions and whole genome amplification from single cells to provide templates for CGH analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2007;2:3173–3184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

