Use of duplex mutation primers for real-time PCR quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum
- PMID: 22087189
- PMCID: PMC3212762
Use of duplex mutation primers for real-time PCR quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in serum
Abstract
Background: The duplex mutation primers offer many advantages over other multi-labeled probes for real-time detection of amplification products.
Objectives: To develop and validate a novel real-time PCR for quantification of HCV RNA based on the duplex mutation primers technology.
Materials and methods: The duplex mutation primers were selected in the highly conservative 5' non-coding region (5'NCR) of the HCV RNA. The assay was validated with the Viral Quality Control panel, which also includes Chinese HCV RNA standards.
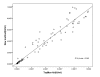
Results: The detection limit was 57 IU/mL, and a good linear correlation in the range of 102-108 IU/mL was revealed (r(2) = 0.999) with the novel method. This assay has a dynamic range of at least 8 log10 without the need for specimen dilution, good clinical intra- and inter-run precision, and excellent correlation with a commercially available assay(r(2) = 0.95).
Conclusions: The high sensitivity, wide linear range, and good reproducibility, combined with low cost, make this novel quantitative HCV real-time PCR assay particularly well suited for application to clinical and epidemiological studies.
Keywords: Duplex mutation primers; HCV; Hepatitis; PCR; Quantification.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of an In-House TaqMan Real Time RT-PCR Assay to Quantify Hepatitis C Virus RNA in Serum and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection.Hepat Mon. 2015 Aug 31;15(8):e28895. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.28895. eCollection 2015 Aug. Hepat Mon. 2015. PMID: 26425128 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a low-cost real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction technique for the detection and quantification of hepatitis C viral load.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010 Jun;48(6):777-84. doi: 10.1515/CCLM.2010.134. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2010. PMID: 20218905
-
Real-time PCR assays for hepatitis B virus DNA quantification may require two different targets.Virol J. 2017 May 12;14(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0759-8. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28494793 Free PMC article.
-
Differences between two real-time PCR-based hepatitis C virus (HCV) assays (RealTime HCV and Cobas AmpliPrep/Cobas TaqMan) and one signal amplification assay (Versant HCV RNA 3.0) for RNA detection and quantification.J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Dec;46(12):3880-91. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00755-08. Epub 2008 Sep 17. J Clin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18799708 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and monitoring of HCV infection using the cobas® HCV test for use on the cobas® 6800/8800 systems.J Clin Virol. 2018 May;102:63-69. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 24. J Clin Virol. 2018. PMID: 29518694
References
-
- Jongerius JM, Sjerps M, Cuijpers HT, van Drimmelen HA, van der Poel CL, Reesink HW, Molijn MH, Peeters GA, Peeters TP, Lelie PN. Validation of the NucliSens Extractor combined with the AmpliScreen HIV version 1.5 and HCV version 2.0 test for application in NAT minipool screening. Transfusion. 2002;42(6):792–7. - PubMed
-
- Wittwer CT, Herrmann MG, Moss AA, Rasmussen RP. Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification. Biotechniques. 1997;22(1):130–1, 4-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
