A plant virus movement protein regulates the Gcn2p kinase in budding yeast
- PMID: 22087310
- PMCID: PMC3210792
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027409
A plant virus movement protein regulates the Gcn2p kinase in budding yeast
Abstract
Virus life cycle heavily depends on their ability to command the host machinery in order to translate their genomes. Animal viruses have been shown to interfere with host translation machinery by expressing viral proteins that either maintain or inhibit eIF2α function by phosphorylation. However, this interference mechanism has not been described for any plant virus yet. Prunnus necrotic ringspot virus (PNRSV) is a serious pathogen of cultivated stone fruit trees. The movement protein (MP) of PNRSV is necessary for the cell-to-cell movement of the virus. By using a yeast-based approach we have found that over-expression of the PNRSV MP caused a severe growth defect in yeast cells. cDNA microarrays analysis carried out to characterise at the molecular level the growth interference phenotype reported the induction of genes related to amino acid deprivation suggesting that expression of MP activates the GCN pathway in yeast cells. Accordingly, PNRSV MP triggered activation of the Gcn2p kinase, as judged by increased eIF2α phosphorylation. Activation of Gcn2p by MP expression required a functional Tor1p kinase, since rapamycin treatment alleviated the yeast cell growth defect and blocked eIF2α phosphorylation triggered by MP expression. Overall, these findings uncover a previously uncharacterised function for PNRSV MP viral protein, and point out at Tor1p and Gcn2p kinases as candidate susceptibility factors for plant viral infections.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
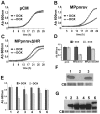
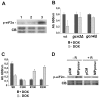
References
-
- Hinnebusch, AG Translational regulation of GCN4 and the general amino acid control of yeast. Ann Rev of Microbiology. 2005;59:407–450. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Dickinson JR, Paul MJ, Halford NG. Molecular cloning of an Arabidopsis homologue of GCN2, a protein kinase involved in co-ordinated response to amino acid starvation. Planta. 2003;217:668–675. - PubMed
-
- Halford, NG Regulation of carbon and amino acid metabolism, roles of sucrose nonfermenting-1-related protein kinase-1 and general control nonderepressible-2-related protein kinase. Ad Bot Res. 2006;43:93–142.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

